What is a Basic Switch?
Basic Switch Definition

A Basic Switch has a micro contact gap and snap-action mechanism∗, and turns ON and OFF with a specified movement and force.
∗Snap-action Mechanism
This is a mechanism that enables instant switching at a fixed operating position, regardless of the operating speed and operating force of the switch.
Features of Basic Switches
| Compact, High-capacity Switching | Because the contacts switch instantly, any arc between the contacts will not continue for a long period of time, which enables the switching of large currents in a small package. |
| High Accuracy | Switching occurs at nearly the same pushing position every time, which allows for high-accuracy position detection. |
| High Durability | Any arcs between the contacts do not last long, which reduces the damage done to the contacts for greater durability. |
| Responsive | Our snap-action mechanism design produces a unique clicking feel and sound for superb operational responsiveness. |
Basic Switches are designed for detection, but can also be used as manual switches.
Basic Switch Models
Basic Switches come in four sizes: General-purpose, Miniature, Subminiature and Ultra Subminiature, depending on the device and scale of the equipment they are to be used in.
We have also added Sealed Basic Switches to the lineup that are designed to provide environmental resistance.

| Basic Switches | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 General-purposeBasic Switches(Z-size) |
 MiniatureBasic Switches(V-size) |
 SubminiatureBasic Switches(S-size) |
 Ultra SubminiatureBasic Switches(J-size) |
| Sealed Basic Switches | |||
 Sealed MiniatureBasic Switches(V-size) |
 Sealed SubminiatureBasic Switches(S-size) |
 Sealed Ultra SubminiatureBasic Switches(J-size) |
|
| General-purpose | Miniature | Subminiature | Ultra Subminiature |
Basic Switches are divided into four size categories: Z, V, S and J.
Z, V, S and J are quoted the marks from NECA classification.
(NECA : Nippon Electric Control Equipment Industries Association)
Basic Switch Structures
Basic Switches consist of five functional sections: actuator, snap-action mechanism, contacts, case and terminals.
Each of these functional sections consists of smaller parts.
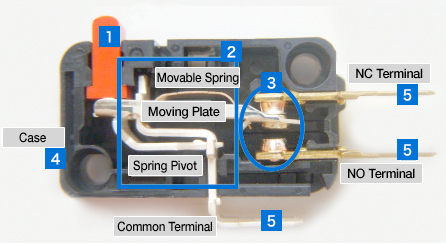
1.Actuator
The actuator relays the external force and movement to the internal mechanisms.
2.Snap-action Mechanism
The snap-action operation is performed by a highly conductive spring.
3.Contacts
The contacts reliably switch electricity to make or break the circuit.
4.Case
The case is highly insulating and mechanically durable to protect the internal mechanisms of the switch.
5.Terminals
The terminals are used to connect to external circuits.
1. Actuator
Many different types of actuators can be attached to the actuator depending on the shape and movement of the detection object, based on a pin plunger.
| Pin Plunger | 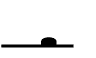 |
Directly relays force and movement to the internal mechanisms of the switch. ⇒This type of actuator can detect with high precision the position of objects that move in short, straight-line strokes. |
| Hinge Lever | 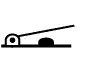 |
The stroke grows larger proportional to the distance away from the fulcrum, while the load grows smaller. ⇒Use this type of actuator for small operating forces or when a large stroke is required. |
| Simulated Roller Lever |  |
|
| Hinge Roller Lever |  |
|
| Leaf Lever |  |
The operating forces is increased because the lever is secured to the fulcrum and must be bent to operate the switch. ⇒The lever returns by itself. This type of actuator is often used in Sealed Basic Switches. |
Select the actuator that is best suited for the shape and movement of the detection object.
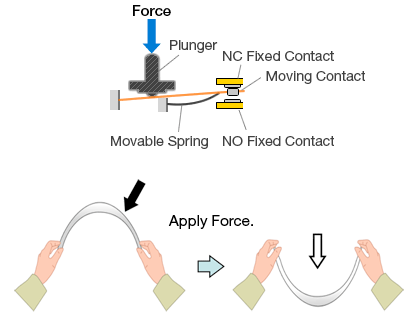
2. Snap-action Mechanism
With a snap-action mechanism, the contacts will instantaneously switch at a specific operating position regardless of the operating speed and operating force of the switch.
As opposed to a snap-action mechanism, with a slow-action mechanism, the operating speed of the switch is always the travel speed of the contacts.
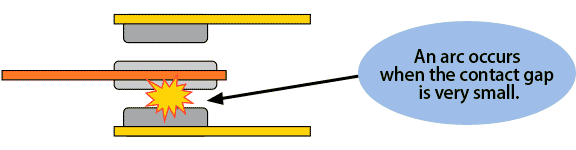
If you press down on the top of a sheet of plastic that is bent info an arc, the sheet will suddenly reverse to a U shape at a certain point. This is like a snap-action mechanism.
Features of Snap-action Operation
- Because the contacts switch at high speed, any arc between the contacts will not continue for a long period of time.
- This reduces contact wear and maintains contact reliability.
- Even small sized switches can make and break large currents.
With AC, the current flow alternates, so arcs are cut off more easily at the same voltage and current in comparison with DC.
Therefore, there is less contact damage with AC.
When pressure is applied to the pushbutton of a switch, the force of the movable spring causes the moving contact to quickly switch from the NC fixed contact to the NO fixed contact.
When pressure is released from the pushbutton of a switch, the force of the movable spring causes the moving contact to quickly switch from the NO fixed contact to the NC fixed contact.
3. Contacts
We also offer a variety of shapes and materials for contacts, and different contact gaps depending on application conditions.
Typical Contact Shapes
Crossbar Contacts for Microloads, Primarily Made of Gold

These contacts have a small contact surface and have high contact pressure per unit area, making them suitable for use with microloads.The primary materials used in these contacts are gold alloy
Rivet Contacts for Medium to High Loads, Primarily Made of Silver
These contacts are used for a wide range of applications from standard to high loads. The primary materials used in these contacts are bronze, silver plating and silver alloy.
Contact Gap
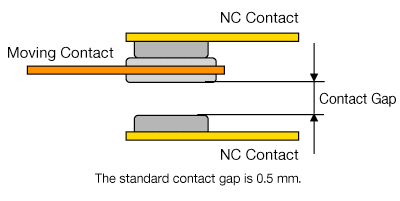
| Code | Contact Gap* | DC Current Shut-off |
Accuracy and Durability |
Vibration and Shock Resistance |
Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | 0.25mm | 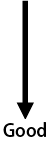 |
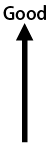 |
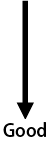 |
High accuracy and high durability |
| G | 0.50mm | General-purpose | |||
| F | 1.00mm | Between G and E | |||
| E | 1.80mm | Vibration and shock resistance |
※The contact gap values are design values.
Select the contact specifications based on the load to switch and application conditions.
4.Basic Switch Cases
Cases are normally made of thermoplastic PBT or thermosetting PF.
Typical Case Materials
| Material Name | Material Symbol | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Phenol resin | PF | A thermosetting resin. It provides superior resistance to combustion and tracking. |
| Polybutyrene terephthalate resin | PBT | A thermoplastic resin. A type of this resin that is reinforced with fiberglass is used for basic switches. |
| Polyamide (nylon) resin | PA | A thermoplastic resin. This type of resin has high heat resistance. It slides well and absorbs water well. |
| Polyphenylene sulfide resin | PPS | A thermoplastic resin. I It provides better resistance to heat than PA. It is used when heat resistance is required, e.g., for soldering. |
Materials are divided into two types: thermosetting resins and thermoplastic resins.
Thermosetting Resin: These resins harden when heat is applied to them. They cannot be reused.
Thermoplastic Resin: These resins melt when heat is applied to them. They can be reformed to recycle the materials.
A thermoplastic resin such as PBT is usually used.
5.Terminals
We also offer a wide variety of terminals.
| Solder Terminals |
Quick-conect Terminals |
Screw Terminals |
PCB Terminals | Molded Lead Wire |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
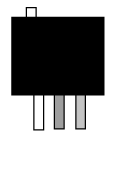 |
| Connect the lead wire by soldering it. | Connect the terminal with a connector. Available sizes: #250, #187, #110, etc." | Connect the lead wire with a screw. | Insert the terminals into PCB and solder it. | Attach the lead wire to the terminal and mold the terminal section with resin. |
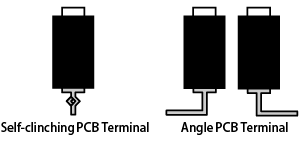
- Bronze alloy is often used in terminals.
- Some terminals use silver plating to increase conductivity. (In some cases, gold plating is used to prevent discoloration due to oxidization and sulfurization.)
- We provide both self-clinching terminals and angle terminals for PCBs.
Each series has its own terminal variations. Select the terminals you need based on your application environment.
Basic Switch Lineup
| Z-size General-Purpose Basic Switches |
V-size Miniature Basic Switches |
S-size Subminiature Basic Switches |
J-size Ultra Subminiature Basic Switche |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Switches | |||
| Z High-capacity Types  |
V Miniature Types  |
SS Subminiature Types  |
D2F Ultra Subminiature Types  |
| A High-capacity Types  |
D3V Miniature Types  |
SS-P Flux-resistant Types  |
J High-capacity Types  |
| X Magnetic Blowout Types  |
VX Low Operating Force Types  |
D3M Connector Types  |
D2MQ Ultra Subminiature Types  |
| DZ DPDT Types  |
D2MV Ultra-low-load Types  |
D2S Flux-resistant Types  |
D2FD Dustproof Types  |
| TZ High-temperature Types  |
D2RV Bilt-in Reed Switch Types  |
||
| D2MC Rotational Operation, Low-torque Types  |
|||
| Z-size General-Purpose Basic Switches |
V-size Miniature Basic Switches |
S-size Subminiature Basic Switches |
J-size Ultra Subminiature Basic Switches |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sealed Basic Switches | |||
| D2VW Miniature Sealed Types  |
D2SW Subminiature Sealed Types  |
D2AW-R Sealed Ultra Subminiature Basic Switch with Integrated Resistors  |
|
| D2SW-P Subminiature Sealed Types  |
D2AW Ultra Subminiature Sealed Type  |
||
| D2FW-G M4-mounting Sealed Types  |
D2HW Long-stroke Sealed Types  |
||
| D2JW Ultra Subminiature Sealed Types  |
|||
| D2QW Ultra Subminiature Sealed Types  |
|||
Basic Switch Applications
Detection Switch Applications
- Open and closed detection for copier machine doors or printer covers
- Open and closed detection for washing machine doors or lids

Copiers

Printers

Washing Machines
Manual Switch Applications
- Mouse click input

Mouse
Note for sale of Automotive relays and using catalogue
- Selling for car makers and companies related to Automotive
Omron and car makers or companies related to automotive confirm relay specifications and actual using condition to use relays safely. Tests are included when necessary.
Omron can not sell or guarantee our automotive relays when we have not finished making contracts with Product Specification. - Selling for NO car makers or companies NOT related to automotive, and individual customers
Basically, Omron can not sell our automotive relays for NO car maker or companies NOT related to automotive.
Omron basically can not support for individual customers. - Safety Precautions for All Automotive Relays
When you consider using our automotive relays or see our catalogue, please confirm our Safety Precautions for All Automotive Relays in advance.
Link for Safety Precautions for All Automotive Relays
DC Power Relay Common Precautions
