International connector safety standards & information
Connector Standards
The connector standard is broadly divided into two categories.
- Specified standards for the connector itself
- Communication standard adopting standard connector and other standards
According to the standard that specifies the connector itself, there are specifications of connector specifications, and specifications up to connector specifications by communication standards.
Specification example defining connectors
- DIN 41612 standard
- DIN standards are defined by the German Institute for Standardization. There are a number of standards which specify connectors, with the DIN 41612 standard (board-to-board connector commonly referred to as a DIN connector) as the most widely known. Other standards also define round connectors.
- MIL-C-83503 standard
- MIL standards are defined by the U.S. Department of Defense. These standards also define standards for various connectors, but the most widely known is the MIL-C-83503 standard (a flat cable connector generally called a MIL connector).
- IEC 61076-4-101 standard
- IEC standards are international standards.
IEC 61076-4-101 is the standard specification for 2 mm pitch HM connectors.
- USB standard
- Although this is a communication standard called Universal Serial Bus, the connector itself is specified within the standard.
Other examples of communication standards that use standard connectors
- VME Bus standard
- The VME Bus (Versa Module Eurocard) standard is a communication standard for rack systems which uses the DIN 41612 connector.
- VME Bus standard
- The VME Bus (Versa Module Eurocard) standard is a communication standard for rack systems which uses the DIN 41612 connector.
- Compact PCI standard
- RS-The Compact PCI standard is a 3U or 6U Eurocard based industrial computer standard.
It uses IEC 61076-4-101 standard HM connectors.
It has its own signal arrangement according to the Compact PCI standard, which does not match the terminal numbers of IEC 61076-4-101.
- RS-232C standard
- RS-232C (Recommended Standard 232 version C) is a standard from EIA, and the official name is TIA/EIA-232-E.
This standard is widely used to connect peripheral equipment such as modems and printers to COM ports, and 25 pole and 9 pole D sub connectors are often used for the terminals.
Safety Standards
Safety standards represent the minimum standards that are required from devices and components to prevent accidents and protect consumers who use electric devices from the hazards presented by electricshock and fire.
Each country has different voltage conditions, weather conditions and safety concepts, and they all adopt their own safety standards.
If the connectors are certified for the safety standards, the connectors are exempt from testing when applying standard certification to devices that use those connectors.
Safety Standards and Certification Bodies by Country
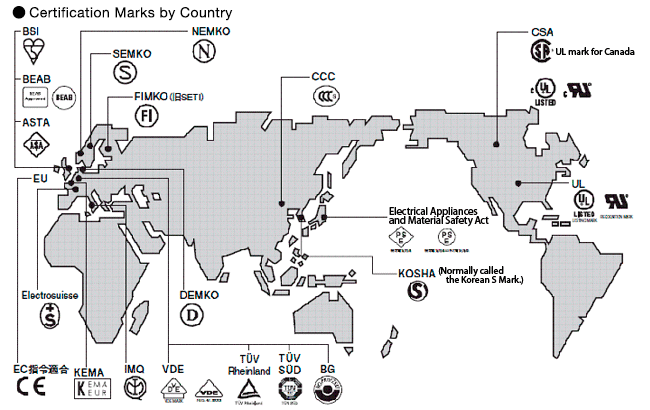
Safety Standards by Country
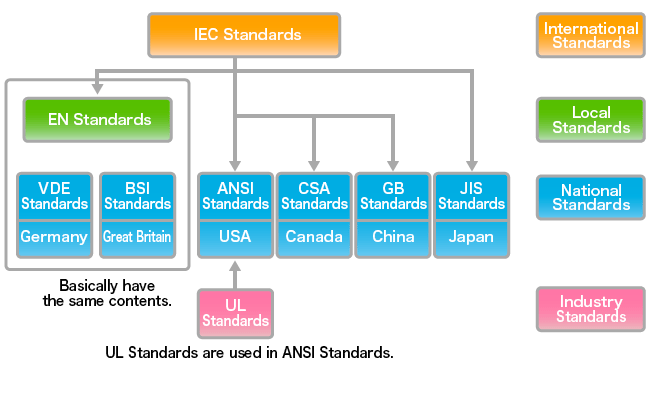
Basic Safety Standard Requirements by Region
North America:
The combustibility and ignitability of the insulation materials used in devices and components and temperature increases are regulated to emphasize the prevention of fires caused by electric devices.
The main standards are UL in the USA and CSA in Canada.
Europe:
The Insulation distances and proof tracking of devices and components are regulated to emphasize the prevention of electric shock accidents caused by electric devices.
The main standards are EN/IEC (Europe/International).
∗Proof Tracking
The proof tracking index is degree of loss of insulation when a carbonized conductive path forms on the surface of an insulation between electric poles with a difference in electric potential.
| Voltage | Accidents | Most Important Requirement | |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 120/240Vac | Fire | Combustibility |
| Europe | 230/400Vac | Electric Shock | Insulation Distance |
Main Safety Standards
| Name | National Standards | Country | Description | Certification Body | Certification Mark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEC | - | International | Technical electric standards based on the most recent scientific technology. Forms the basis for standards in other countries. | - | - |
| UL | ANSI Standards |
United States | To prevent fires, standards are enforced for the sale of electric products in the USA by state and city. Components must also be certified. |
UL |   |
| CSA | CSA Standards |
Canada | North American safety standards are applied and operated to prevent fire accidents, in the same way as in the USA. | CSA |  |
| EU | EN Standards |
Europe | Standards are designed to prevent electric shock and fires, but are not legally enforced. Enforcement is achieved through strict penalties. |
VDE, TUV-Rh |   |
| CCC | Chinese National Standards: |
China | Items for which certification is enforced are specified, and the import and sale of uncertified items in China is prohibited. | CCC |   |