Winner of MONODZUKURI Innovative Parts and Components Award 2021
(Only applicable to G9KA-1A)
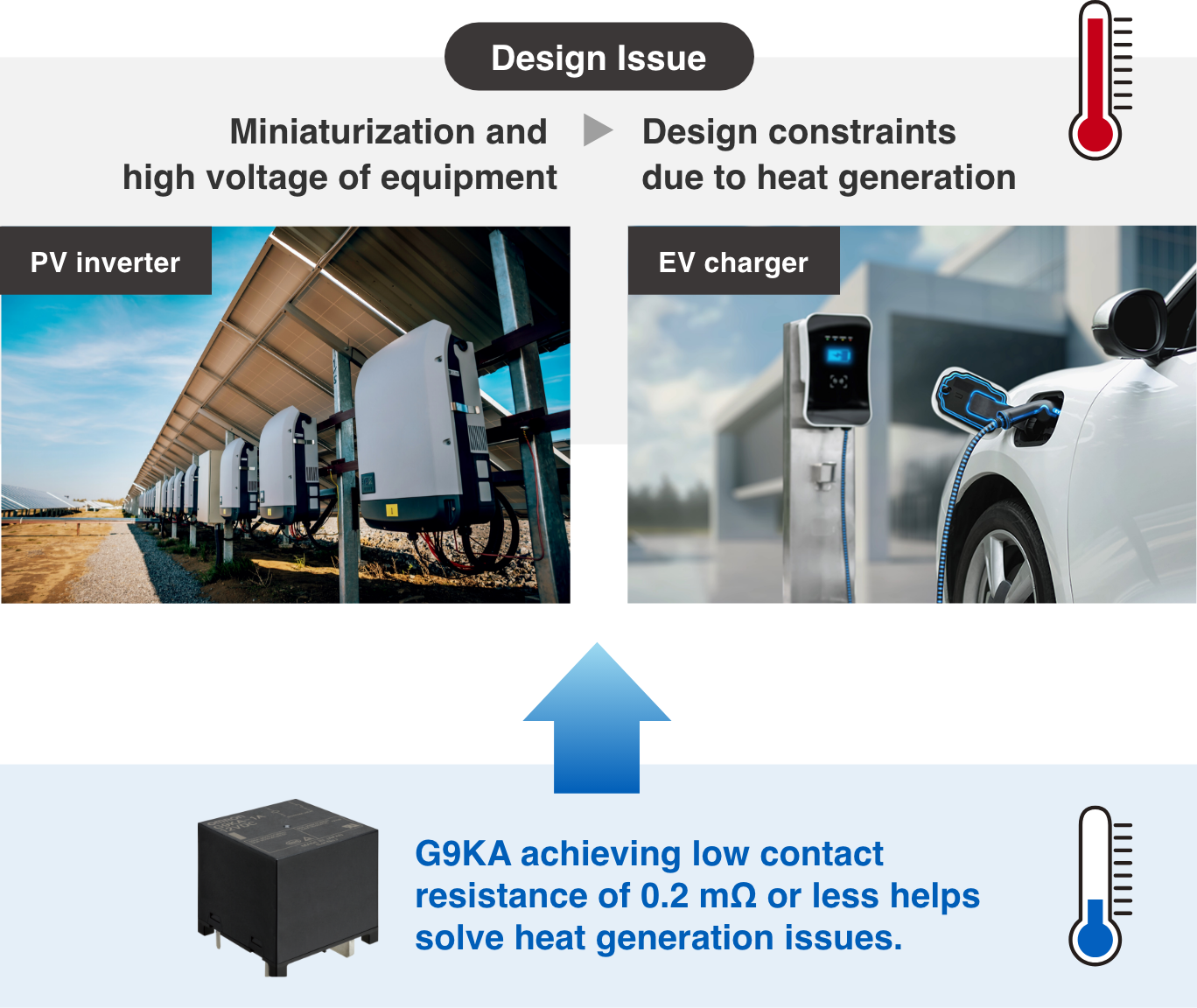
Next-generation energy devices such as EV chargers, PV inverters, and energy storage systems are becoming increasingly high-voltage and high-current.
Due the trend, relays play an important role in circuit control, but conventional relays pose risks such as heat generation and damage to the circuit board due to high currents.
To address this issue, OMRON’s G9KA minimizes heat generation while providing high capacity by suppressing contact resistance to 0.2 mΩ or less.
This reduces the amount of work required for heat dissipation design, while simultaneously achieving smaller equipment, higher reliability, and lower costs.
OMRON supports the future of next-generation energy devices with its highly reliable products.
↓Click to check some of the content
In recent years, there have been changes in solar power systems to meet demands. The trend is shifting from centralized systems to decentralized systems as a more stable power supply is required to counter disaster risks such as earthquakes and floods. By distributing power conversion across multiple power conditioner instead of using a single power conditioner, the risk of power generation being halted due to equipment failure can be reduced even in the event of a disaster. Furthermore, individual facilities and equipment are now required to operate efficiently by increasing power generation efficiency through higher capacity and higher current, and by suppressing capital investment through downsizing and weight reduction.
As downsizing and higher capacities continue to advance, the urgent issue is to reduce the heat generated by the equipment itself, which is a factor in energy loss and reduction of the equipment's service life.

A barrier to downsizing and higher capacity is the heat generated in the equipment.
If the current doubles due to higher capacity, the amount of heat generated will quadruple.
The heat generated by the equipment can cause malfunctions and shorten the life of the PCB. Therefore, relays that carry large currents in the 200-300A class require heat dissipation mechanisms such as fans and heat sinks, and the devices themselves tend to be large in size.
![[Heat generation = Current2 x Resistance]100A relay->(Amount of heat generated quadruples)200A relay](/eu-en/sites/components.omron.com.eu/files/2022-11/g9ka_lp_01_03_en.png)
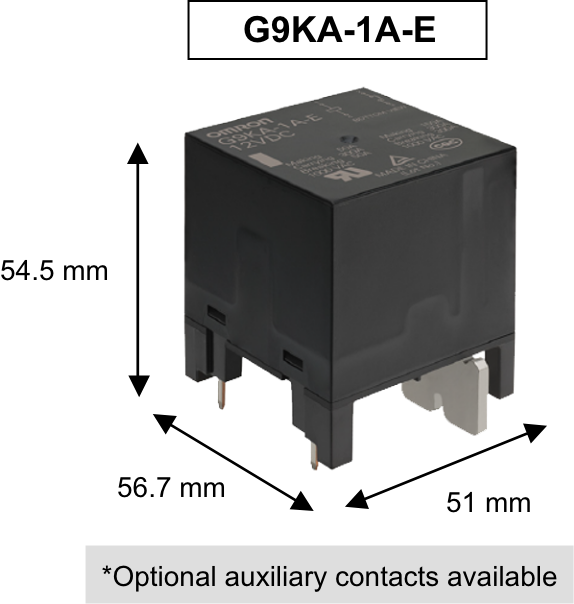
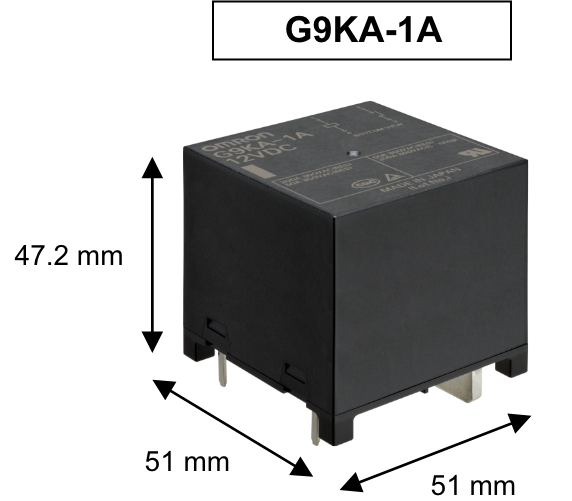


The G9KA high-capacity power relay was developed to solve this heat generation problem. G9KA's industry-leading* ultra-low contact resistance of 0.2 mΩ max suppresses heat generation, a major challenge in downsizing and high capacity.
* According to OMRON’s research in July 2021
It’s compact size is about 1/3 of the height compared to contactors of similar current capacity, contributes to downsizing and space saving of equipment.
![Contactor applied:H approx. 140 mm / PCB relay applied(G9KA-1A):H approx. 47 mm[Height approx. 1/3]](/eu-en/sites/components.omron.com.eu/files/2023-04/g9ka_lp_01_05_en.png)
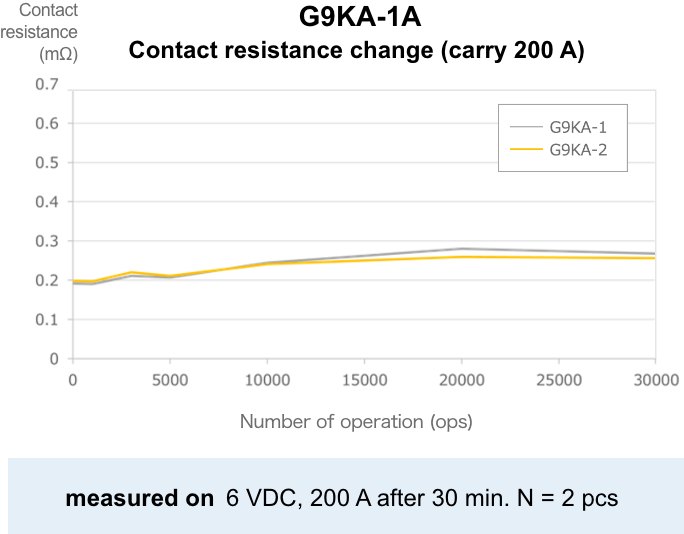
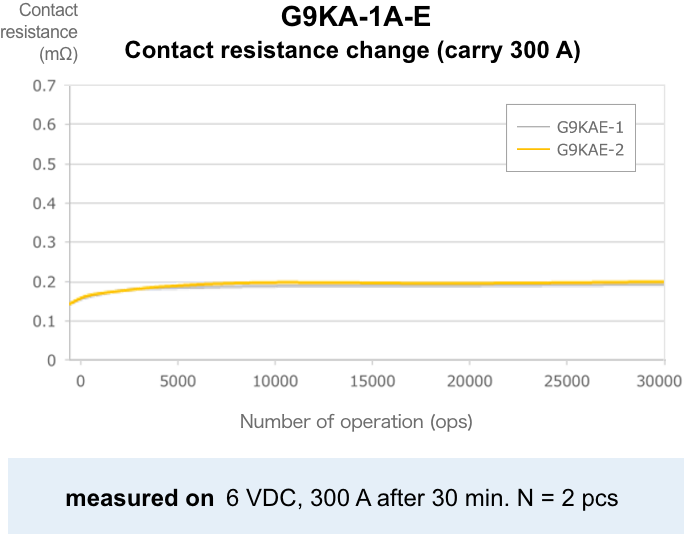
The lower the contact resistance, the less heat is generated. In contrast to conventional high-capacity relays with an initial contact resistance of 1 to 5 mΩ (actual value of about 0.4 mΩ), G9KA has reduced the standard value to 0.2 mΩ max, 1/5 of the standard value, by reducing the center value and variation.
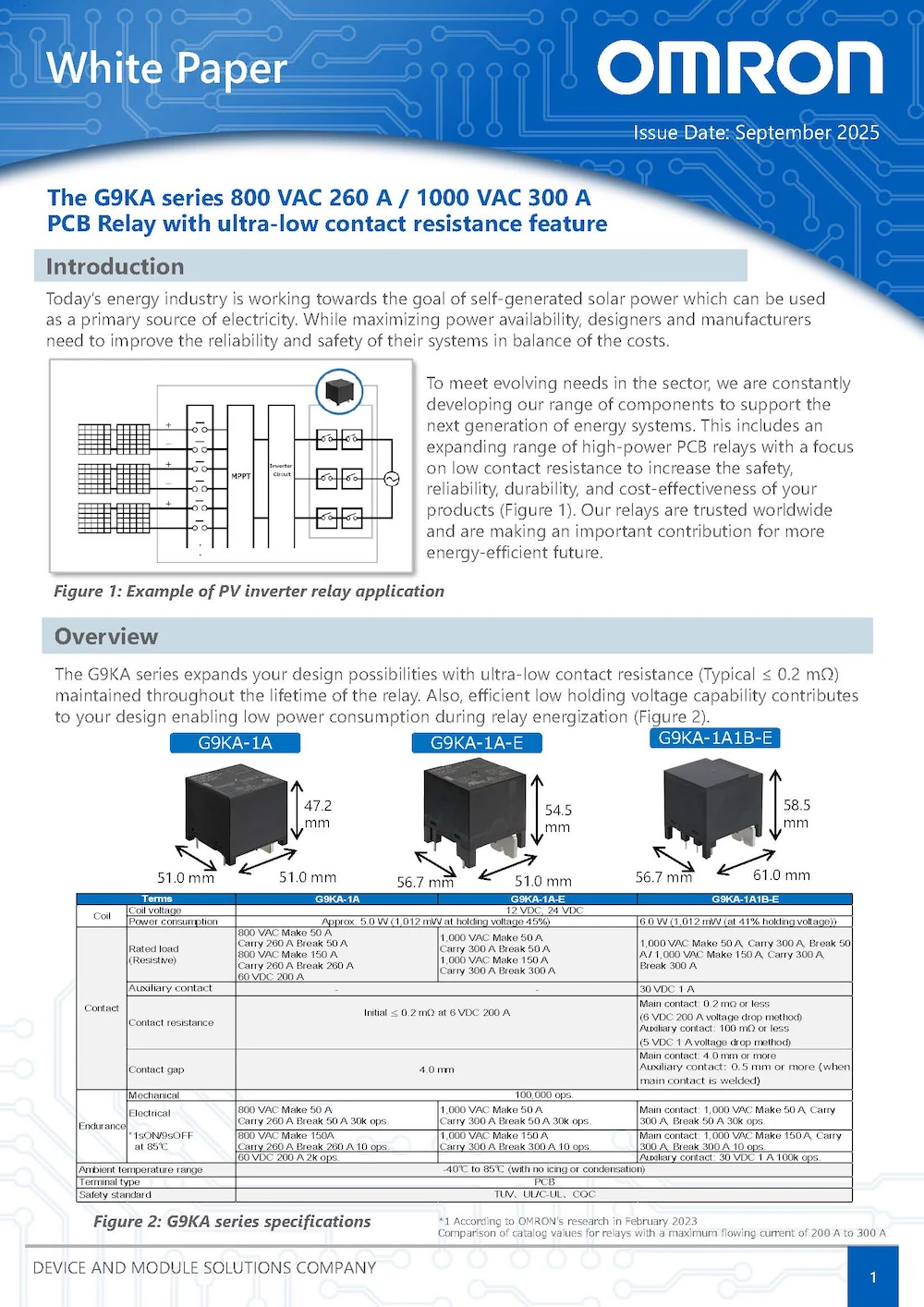
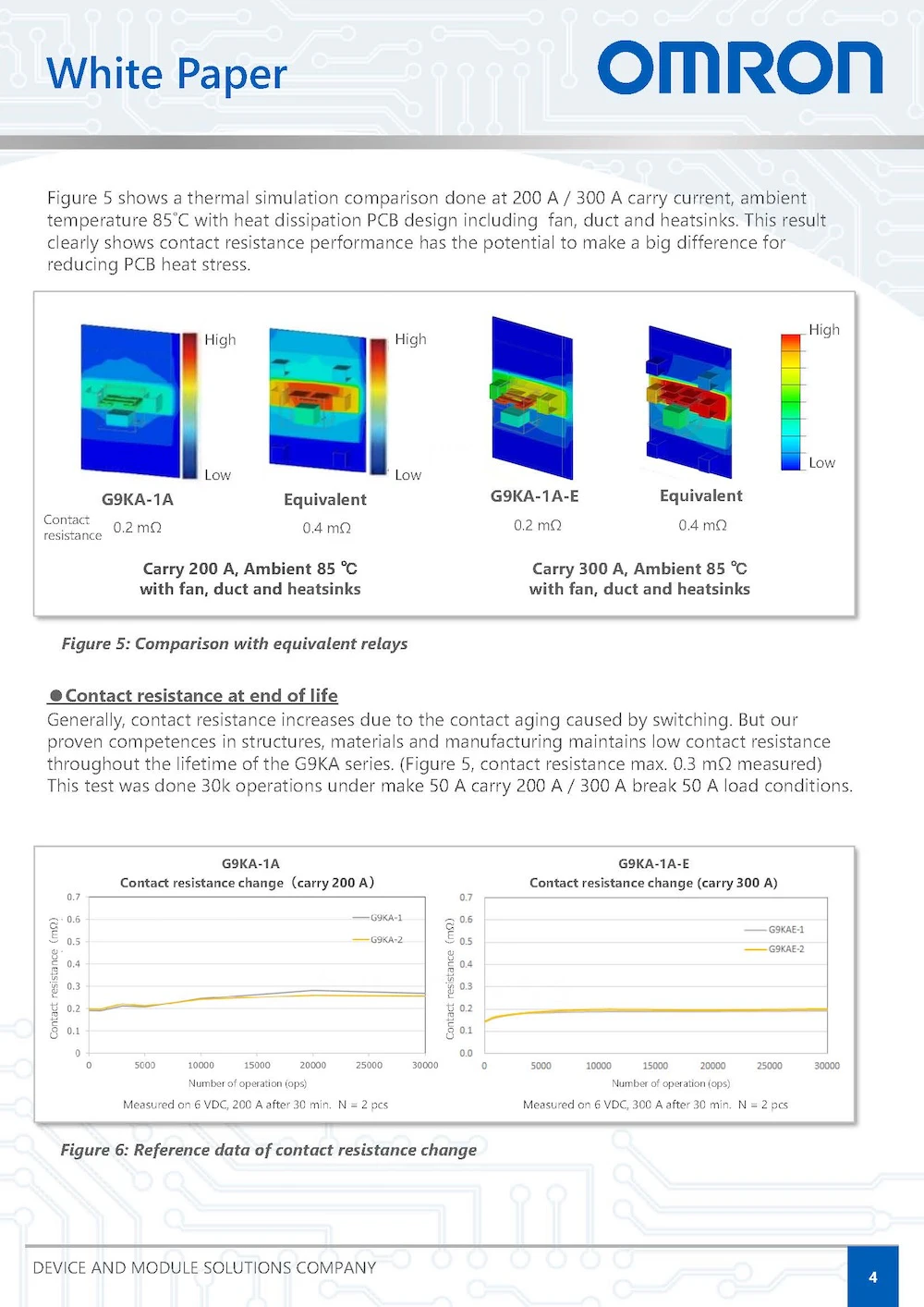
As a result, the temperature rise can be reduced by about 30% compared to relays with comparable general performance. Furthermore, it maintains stable contact resistance (reference value) in switching durability evaluation, and contributes to heat generation issues with significantly lower contact resistance compared to conventional relays with equivalent performance.
Initial contact resistance is
industry-leading* 0.2 mΩ max
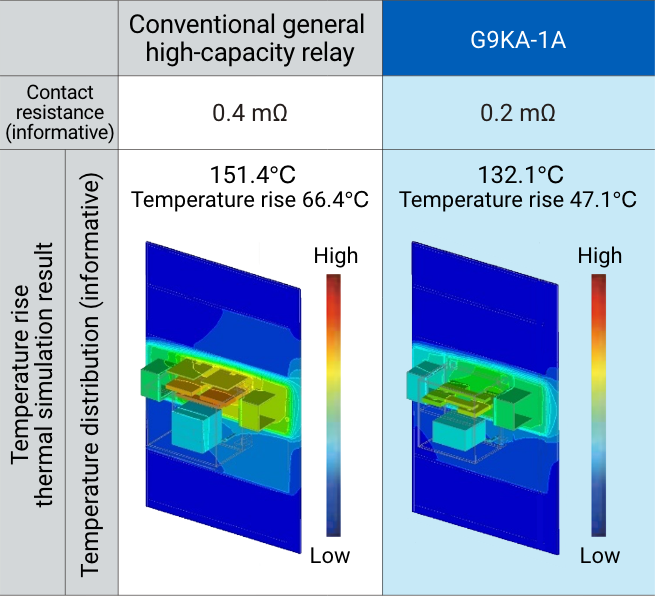
< Simulation conditions >
480 VAC/200A, ambient temperature 85°C, fans, ducts, and heat sinks used, one on board.
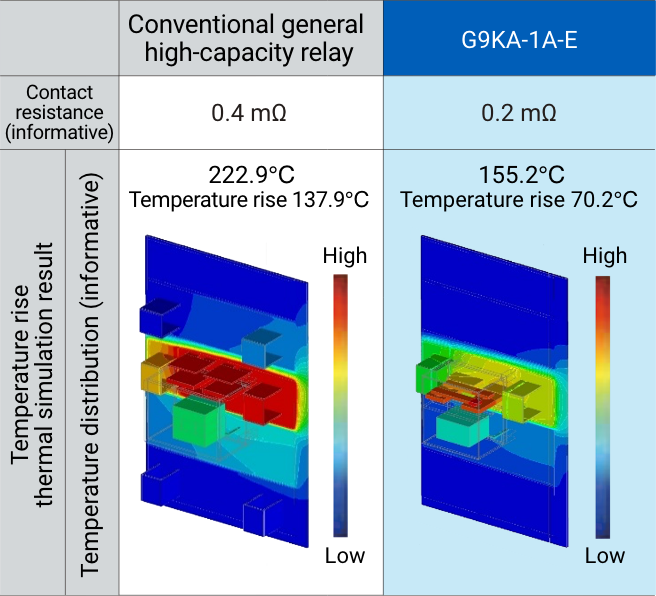
< Simulation conditions >
480 VAC/300A, ambient temperature 85°C, fans, ducts, and heat sinks used, one on board.
* According to OMRON’s research in July 2021
Contact resistance of 0.3 mΩ max maintained even after
electrical durability testing
G9KA can solve a variety of customer problems because it "generates less heat".
Its low heat generation allows for a high-capacity design of 800V/200A at a size of 51 x 51 x 47.2 mm, 1000V/300A at a size of 56.7×51×54.5mm without worrying about heat generation issues.
Its low heat generation reduces PCB damage and energy loss due to thermal stress.
Its low heat generation reduces the need for heat dissipation designs such as fans and heat sinks, thereby reducing design man-hours, equipment size, and costs.
![[Because of its low heat generation]Long life:Reduced PCB damage due to heat generation extends machine life、Cost reduction:Reduction of heat dissipation mechanism and replacement from contactors enables product downsizing and cost reduction、Higher design efficiency:Simpler design by reducing the heat dissipation mechanisms such as fans and heat sinks, thereby reducing the time and man-hours required for heat dissipation design.、Supporting high capacity applications:Energizing and de-energizing 800V/200A, 1000V/300A far exceeding the specifications of OMRON's existing high-capacity products、Energy-saving:Higher power generation efficiency by reducing energy waste due to heat generation(Gets hot and parts break down>Need to limit the output of the power conditioner>Low power generation efficiency:Energy is lost by turning into thermal energy、Downsizing:Simplified heat dissipation structure reduces PCB area](/eu-en/sites/components.omron.com.eu/files/2023-04/g9ka_lp_03_02_en.png)
OMRON has realized two contradictory performances, "high capacity 800V/200A, 1000V/300A" and "low heat generation", by combining OMRON's long-standing technical know-how.
![[Low contact resistance]Pure Ag < Ag + Additive、[High weldability]Pure Ag > Ag + Additive](/eu-en/sites/components.omron.com.eu/files/2022-11/g9ka_lp_04_04_en.png)
To achieve the targeted low contact resistance, G9KA uses pure Ag-based contacts with Ag content of 99% or higher.
In general, the contact resistance is pure Ag contacts
Ag contacts with additives, but the opposite is true for weld resistance. In conventional relays used for switching loads, contact welding due to arcing was prevented by selecting contact materials with additives, but the contact resistance increased to several tens of mΩ.
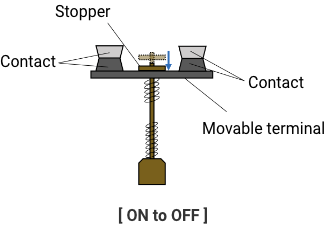
G9KA uses a plunger-type relay structure to prevent contact welding.
The impact force generated by the stopper being swung down like a hammer ensures that the weld can be pulled away, thus realizing reliable contact stripping even for contact materials that are prone to welding.
G9KA uses a bifurcated contact structure. By paralleling the current paths, the current can be shunted and the heat generation can be suppressed by reducing the current per path.
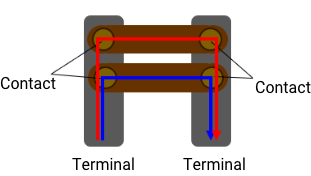
[Single contact]

【Heat generation】
Qsgl = CR1*(200A)2*t
= CR1*4*104 *t
[Bifurcated contact]
【Heat generation】
= Amount of heat generated 1/2
Qtwn = CR1*(100A)2 *t *2 contacts
= CR1*2*104*t
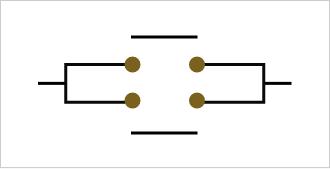
G9KA uses a double-break structure for its switching.
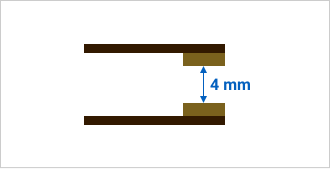
The cutoff performance of a contact is determined by the contact spacing. For high-capacity PV inverters, the standard requires a contact spacing of 3.6 mm or more. The greater the distance between contacts, the larger the coil that drives the relay. The double-break structure has two contact points, effectively doubling the contact spacing. Without increasing the size of the coil, it is now possible to energize and de-energize 800V/200A, 1000V/300A in a compact size.
【Single break structure】
【Double break structure】
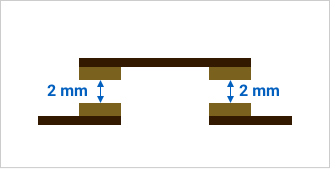
Ensuring contact spacing of 4 mm in total
![]() Auxiliary contact option is available.
Auxiliary contact option is available.
Please consider this for applications that require welding detection.
(Example: Matrix switches for quick chargers, etc.)
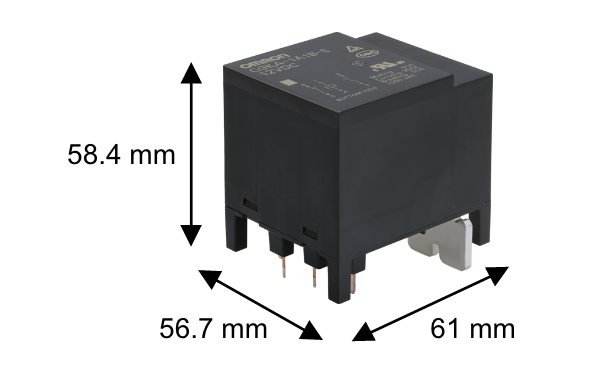
G9KA-1A1B-E
Auxiliary contact:1b (N.C.)
Mirror contact structure* adopted
(IEC/EN 60947-4-1 compliant)
Mirror contact structure (image diagram)
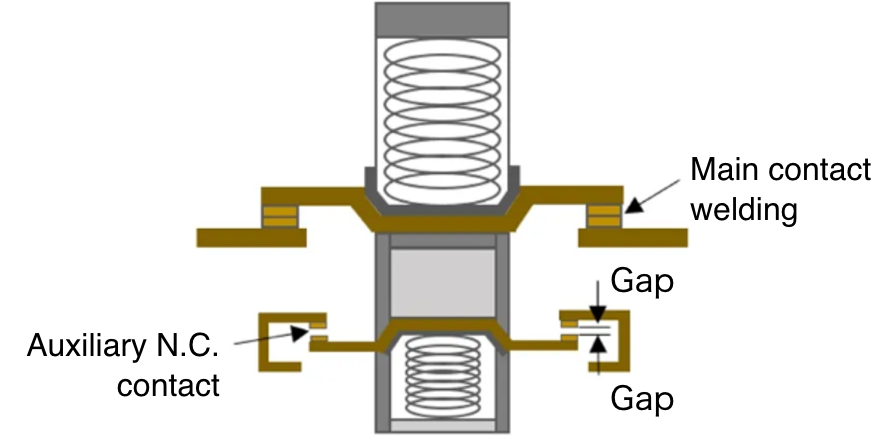

* The mirror contact structure satisfies the impact withstand voltage of 2.5 kV or more for all N.C. contacts of the auxiliary contact block even when the coil is de-energized, or ensures a contact gap of 0.5 mm or more, if the N.O. contact (main contact) of the relay becomes welded in the combination of a relay and an auxiliary contact block.
How about OMRON's G9KA for devices that require "high capacity but generate as little heat as possible"?

Power conditioners for industrial photovoltaic power generation

EV quick charger

Robot control equipment

Power storage system (ESS, UPS)

Industrial air conditioning
↓Click to check some of the content