Relay Basics: Technology
- Basics
- Technology
- Applications
- Standards
- Glossary
Types of Coils
Coils are classified according to the types of magnetic circuits and operational functions.
1. Magnetic circuit
Non-polarized: Operating coils do not have polarity
Polarized: Operating coils have polarity
2. Basic Function
Relay is classified into two basic functions: single-side stable relay and latching relay (also called "Keep" relay)
Single-Side Stable Relay
The contacts turn ON or OFF only when an input signal is received.
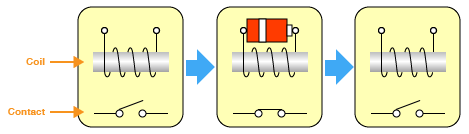
Latching (Keep) Relay
The contacts turn ON or OFF when an input signal is received but maintains its contact position during power interruptions.
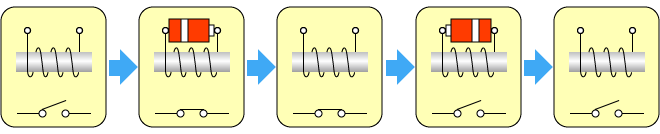
Select the optimal relay that meets your application and sequence requirements.
Types of Contacts for Electrical Relays
Contacts are classified according to the types of contact forms and contact reliabilities.
1. Contact Forms
There are three types of contact forms: Form A contacts, Form B contacts, and Form C contacts.
Form A contacts ("Make contacts")
This is normally open contact and closes when a voltage is applied to the coil.
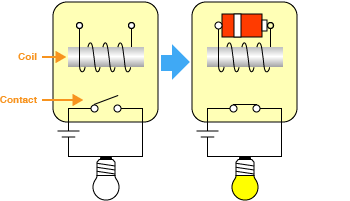
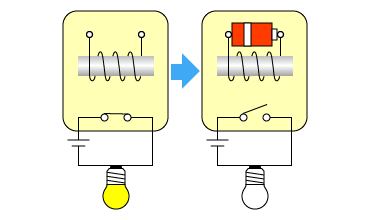
Form B contacts ("Break contacts")
This is normally closed contact and opens when a voltage is applied to the coil.
Form C contacts ("Transfer contacts")
Combines the Form A and Form B contacts in a single relay and when a voltage is applied to the coil, Form C contact moves away from Form B contact and connects with Form A contact (for single-side stable relays).
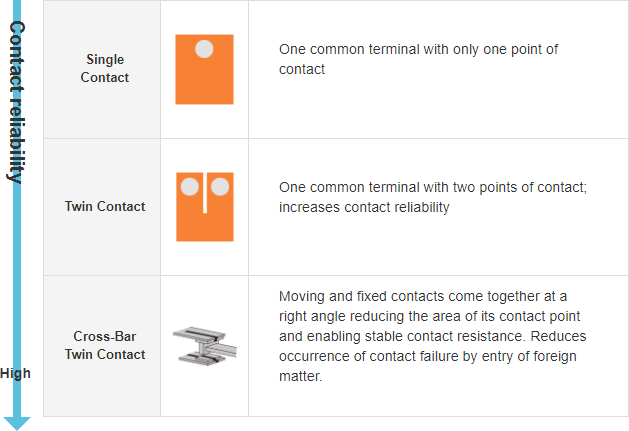
2. Electrical Relay Contact Reliability
Contact configurations are classified into three types according to the reliability level: Single contact, Twin contact and Cross-bar Twin contact.
Types of Terminals for Electrical Relays
The terminal configurations are classified as follows:
| Types of Terminal | Terminal configuration | Typical Relay Model |
|---|---|---|
| Plug-in terminal | 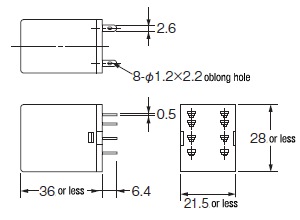 on maintenance,Lineup of dedicated sockets |
 MY |
| PC board terminal | 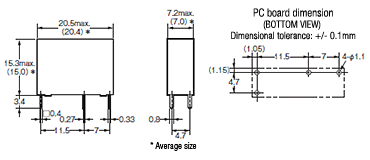 PC board (through hole) mount type |
 G5NB |
| Screw terminal | 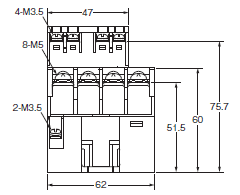 Emphasis on maintenance,Screw terminal connection |
 G7Z |
| Surface-mount terminal |  PC board (surface-mount) automatic mount type |
 G6K(-F/G) |
| Quick connect terminal | 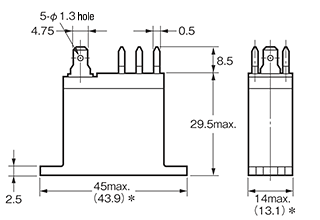 Emphasis on maintenance,Tab terminal connection |
 G2R-T |
Enclosures for Electrical Relays
The terminal configurations are classified as follows:
× : Penetration exist
○ : No penetration
△ : Penetration may exist
| Enclosures | Characteristics | Atmosphere Conditions | Typical Relay Models | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dust and dirt | Harmful gas | |||
| Flux resistant type(PCB relay) | This type of structure prevents solder flux penetration into the interior. | △(Protects from large amounts of dirt and dust) | × |  G2R |
| Palstic Sealed(PCB Relay) | This type of structure prevents solder flux and cleaning solvent penetration. | ○ | ○ |  G5Q |
| Unsealed(Plug-in Relay) | This type of structure places the relay inside a case to protect against foreign substances. | △ | × |  MY |
| Plastic Sealed(Plug-in relay) | This type of structure places the relay with resin case and cover to minimize corrosion effects. | ○ | ○ |  MYQ |
| Hermetically sealed(Plug-in relay) | This type of structure places the relay in a corrosion resistant sealed case using metal or glass purged with inert gas (N2) to protect from corrosive gas penetration. | ○ | ○ |  MYH |
- Basics
- Technology
- Applications
- Standards
- Glossary

