Fundamentals of MOS FET Relays (No Movable Contacts): Basics
- Basics
- Technology
- General Application
- Glossary
What is a MOS FET Relay?
A relay is a component that receives electrical signals from outside sources and turns on/off or switches electrical circuits. It is mainly used when electrical isolation between the input-side and output-side circuits is desired, thereby reducing noise effects and safety risks.

MOS FET relays are non-contact relays that use MOS FETs (metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors) to switch control signals.
MOS FETs are sometimes called photocouplers as a type of coupler, but because they are relatively new products, each company has given them various names and trademarks.
The table below shows examples of products equivalent to our MOS FET relay (G3VM).
According to Omron's research: as of December 2023
| Manufacturer | Catalog name |
|---|---|
| Toshiba | Photorelay |
| Panasonic | PhotoMos relay |
| Okita Works | PhotoDMOS-FET relay |
| Omron | MOS FET relay |
| Infineon Technologies | Solid state relay |
| BROADCOM | Solid-state relay |
Note: Other company names and product/service names may be used as trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
How is a MOS FET Relay Positioned?
Relay technology can be divided into two main categories: Movable contacts (mechanical relay) and no movable contacts (solid state relay). MOS FET relays are among the no movable relays.
Movable contacts (Mechanical Relay)

Characteristics
This type of relay has contacts that are mechanically actuated to open/close by a magnetic force to switch signals, currents and voltages ON or OFF.
No movable contacts
Characteristics
Unlike mechanical relays, this type of relay has no moving contacts but instead employs semiconductor and electrical switching elements. By the operation of these electronic circuits, signals, currents and voltages are switched ON or OFF electronically.
MOS FET relays
Semiconductor relays for printed circuit boards (PCBs) using MOS FETs as output elements

Solid State relays
Semiconductor relays for power switching in control panels and PCBs, using phototriacs, phototransistors, and photocouplers for insulation between input and output.
What are the Types of MOS FET Relays?
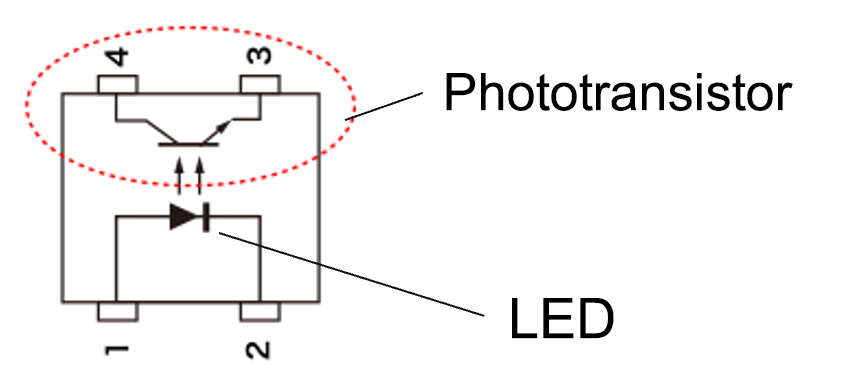
MOS FET relays are non-contact relays (solid-state relays) and can be classified as a type of photocoupler because they are components consisting of a light emitting diode (LED) and a light receiving element. There are three major types of photocouplers, and the primary difference is the type of light-receiving element used.
MOS FET relays are products that incorporate a PDA (Photodiode Array) and a MOS FET chip in the light receiving element.
Photocoupler: LED (light emitting diode) + Light receiving element
Transistor coupler
LED + Light receiving element (phototransistor)
A transistor that is operated by light. It is unidirectional and can only control direct current. Output characteristics depend on the input current value.
Triac coupler
LED + Light receiving element (phototriac)
A triac that is operated by light. It is bidirectional and can control alternating current. Once triggered, the output current remains ON until it reaches zero, so DC cannot be interrupted.
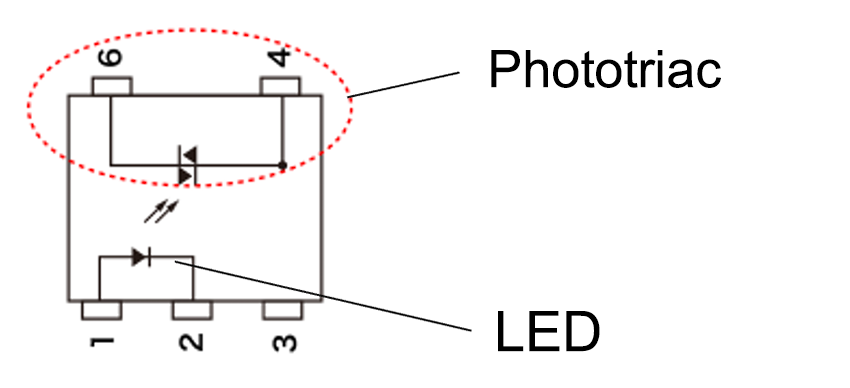
MOS FET relay
LED + Light receiving element (PDA + MOS FET)
A MOS FET that is operated by light. It can control both direct current and alternating current. Output characteristics do not depend on the input current value. Some models can also switch ampere-level currents with small input currents.
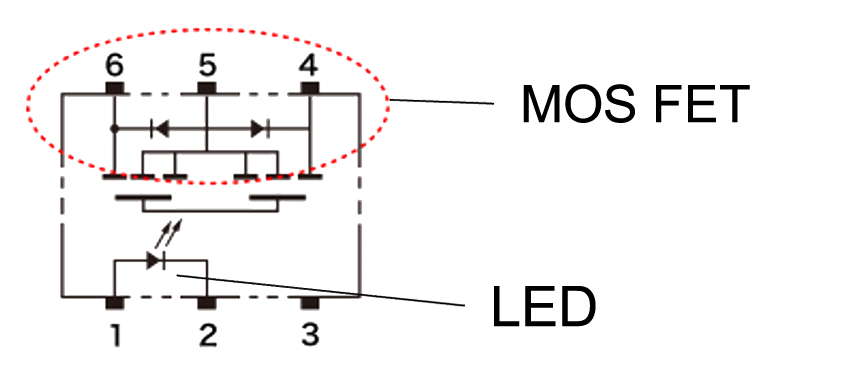
What are the Structure and Principles of MOS FET Relays?
MOS FET relays are semiconductor relays that use MOS FETs as output elements to switch signals. Unlike mechanical relays that use movable contacts to open and close circuits, MOS FET relays are contactless and have advantages over mechanical relays, such as fast response, compact size, long life, and quiet operation.
MOS FET relay structure
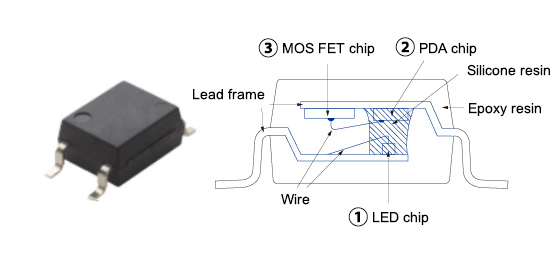
- ① LED chip
- Semiconductor device that emits light
- Emits light according to the input current
- ② PDA chip (photodiode array)
- Photodiode array (solar cell + control circuit)
- Semiconductor device that detects light and generates electricity
- Generates electricity according to the amount of light received to supply the gate voltage for the MOS FET chip
- ③ MOS FET chip
- A type of transistor
- Driven according to the voltage of PDA chip
- Switches signals on electronic circuits
MOS FET Relay Operating Principle
Operating principle and function of MOS FET relay
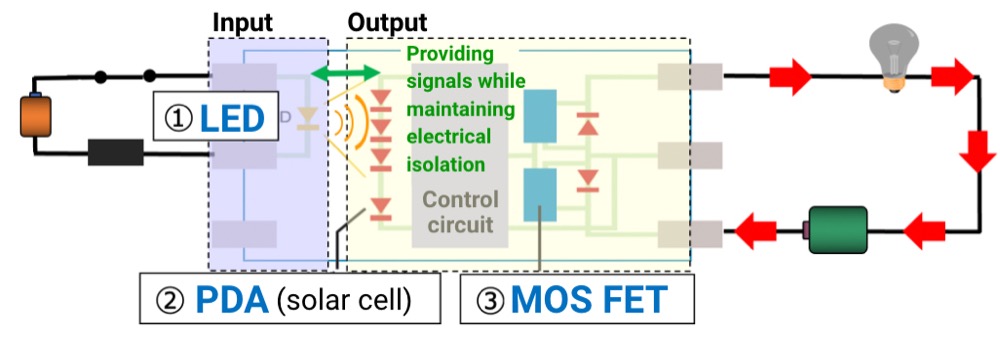
- ① LED
- The LED emits light when current is applied to the input side.
- ② PDA
- The PDA on the output side receives the light and generates electricity, which is then converted back into voltage.
- ③ MOS FET
- The voltage generated by the PDA goes through the control circuit to become the gate voltage, which drives the MOS FET.
What are the Drive Systems for MOS FET Relays?
MOS FET relays can be controlled in two major ways.
- ・Current drive system (MOS FET relays in general)
- This product can be used at the optimum drive current by designing the limiting resistor according to the drive voltage.
- ・Voltage drive system (some MOS FET relay series)
- This product saves space and eliminates the need for input-side resistor selection by incorporating the limiting resistor required for drive current control.
How are MOS FET Contacted Configured?
As shown in the table below, there are two types of MOS FET relays: SPST-NO (1a) and SPST-NC (1b).
| Input current | SPST-NO (1a) | SPST-NC (1b) |
|---|---|---|
| Not energized | 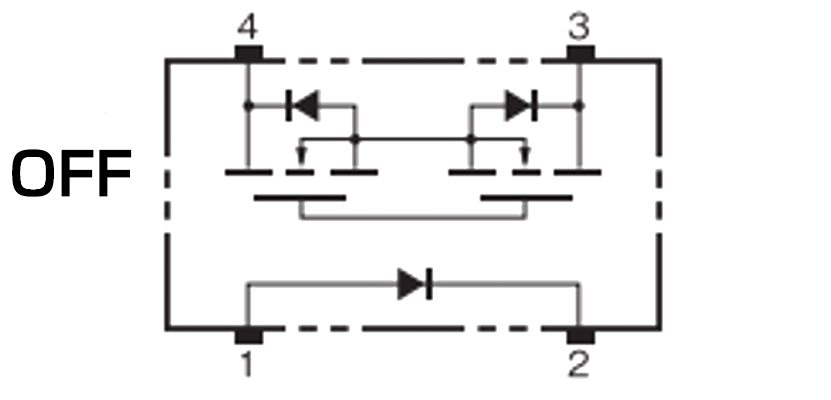 |
 |
| Energized | 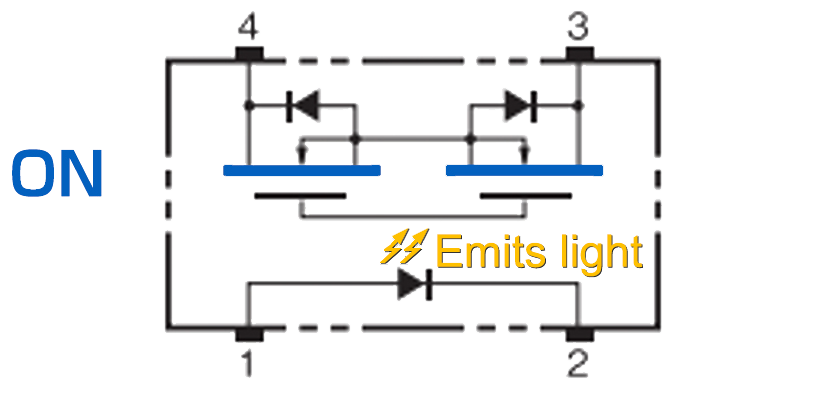 |
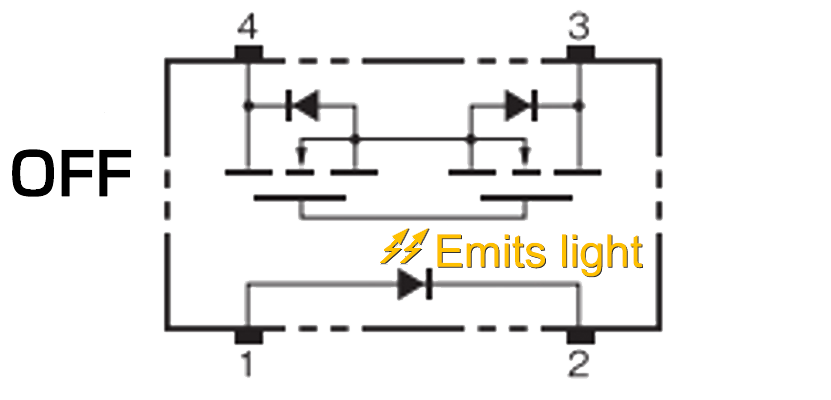 |
If you require SPDT, please consider the G3VM-M series of module type that realizes SPDT contact configuration.
How are MOS FET Relays Connected?
MOS FET relays can handle both direct current and alternating current by incorporating two MOS FET chips.
In addition, the 6-pin MOS FET relay type offers the following advantages by changing the connection method of the output-side terminals.
| Connection | Features | Applicable load |
|---|---|---|
|
Connection A 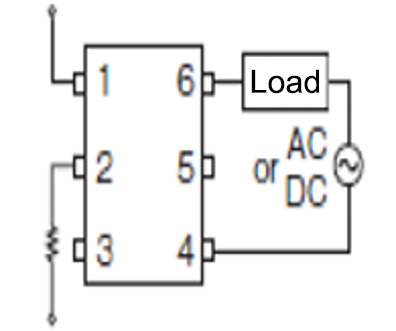
|
Can handle both DC and AC 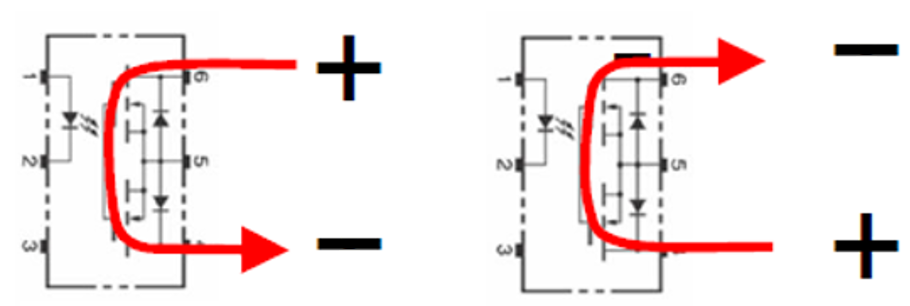
|
DC |
|
Connection B 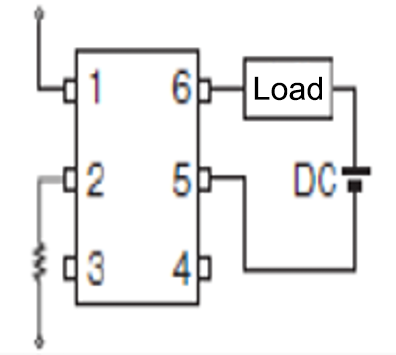
|
On-resistance can be lowered 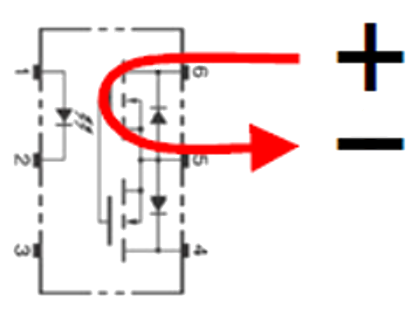
|
DC |
|
Connection C 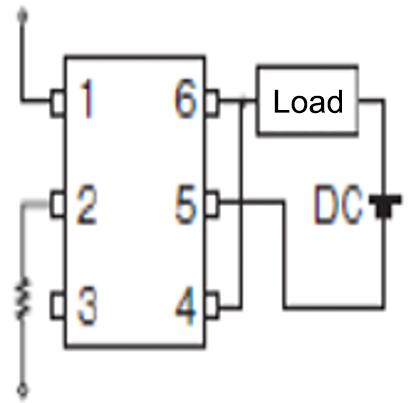
|
Load current can be increased 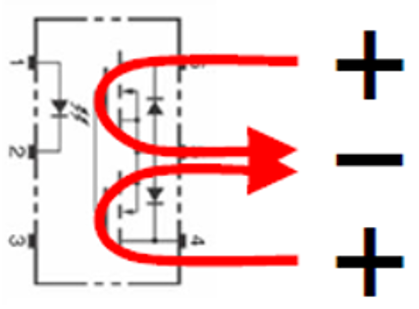
|
DC |
What are Features of MOS FET Relays?
The followings are characteristics that are unique to the function of turning on/off or switching electrical circuits.
- Ultra-compact & lightweight
- Long life
- Stable ON resistance
- Quiet operation
- Fast response
- High withstand voltage, etc.

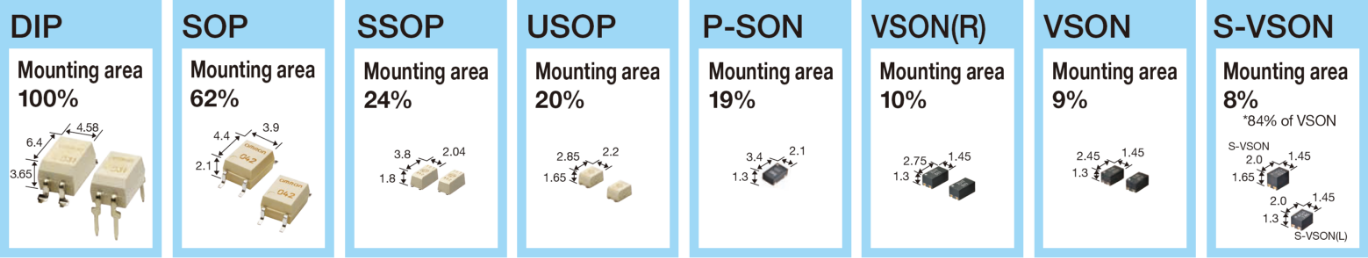
Ultra-compact & lightweight
Small packages centered on VSON and S-VSON contributes to the miniaturization and high density of the entire device.
Long life
The contactless structure with optical signal transmission system eliminates life deterioration due to contact wear and tear, contributing to reduced maintenance frequency.
Stable ON resistance
The contactless structure with optical signal transmission system eliminates mechanical wear and tear phenomena, thus maintaining stable resistance values.
Low power consumption
Extremely low power consumption on the input side contributes to energy saving of equipment.
Quiet operation
The contactless structure eliminates opening and closing noises when in use, contributing to quiet operation of equipment.
Fast response
Fast response with an operating time of 0.2 ms (SSOP, USOP, VSON).
Load voltage
Compact yet capable of switching high-voltage loads, contributing to space saving even in high-voltage circuits.
The lineup includes products with a maximum load voltage of 600V.
Dielectric strength
The input-output withstand voltage of 2500 VAC is secured, and a series of 5000V products with high withstand voltage is also available.
For further details, please refer to the following.
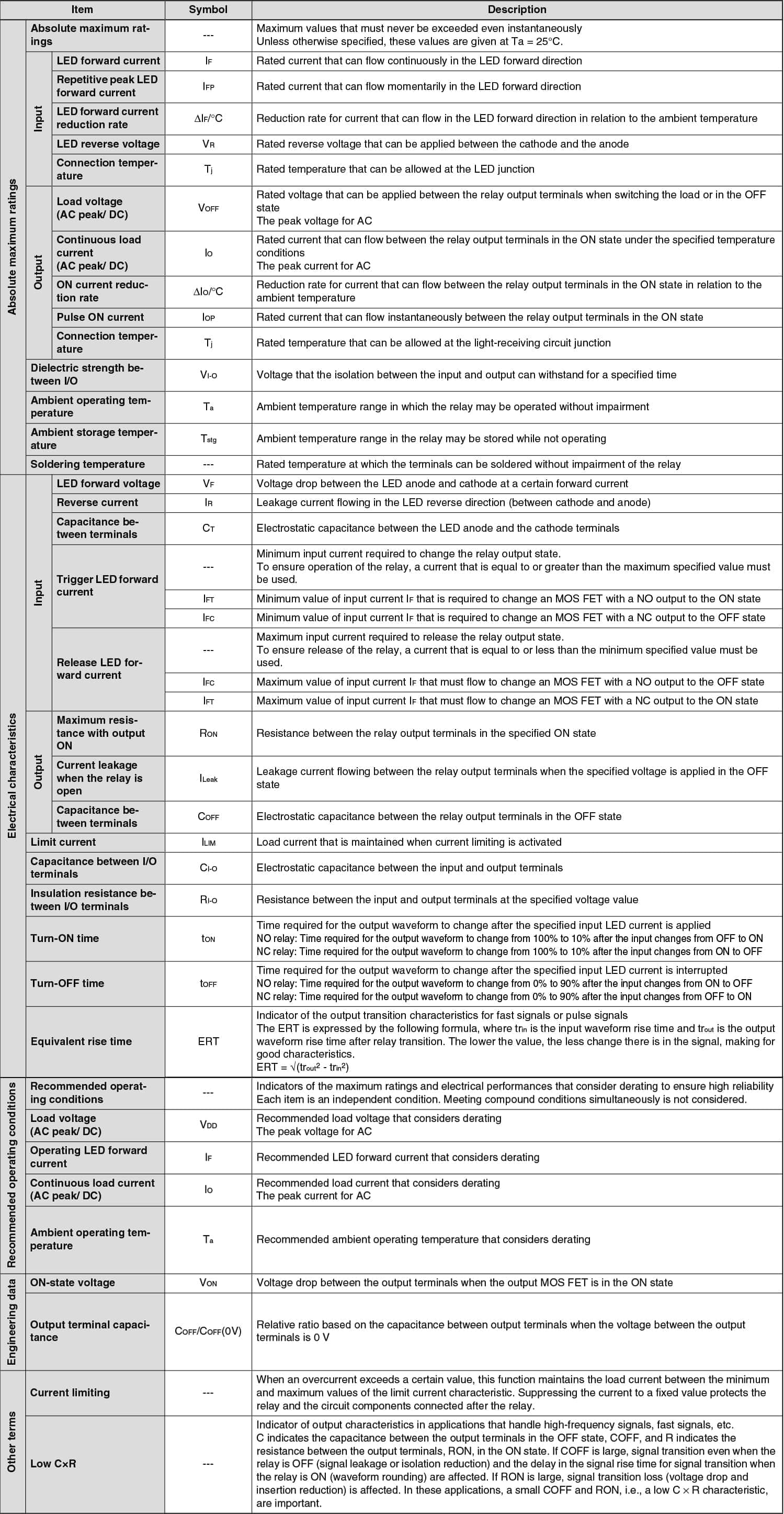
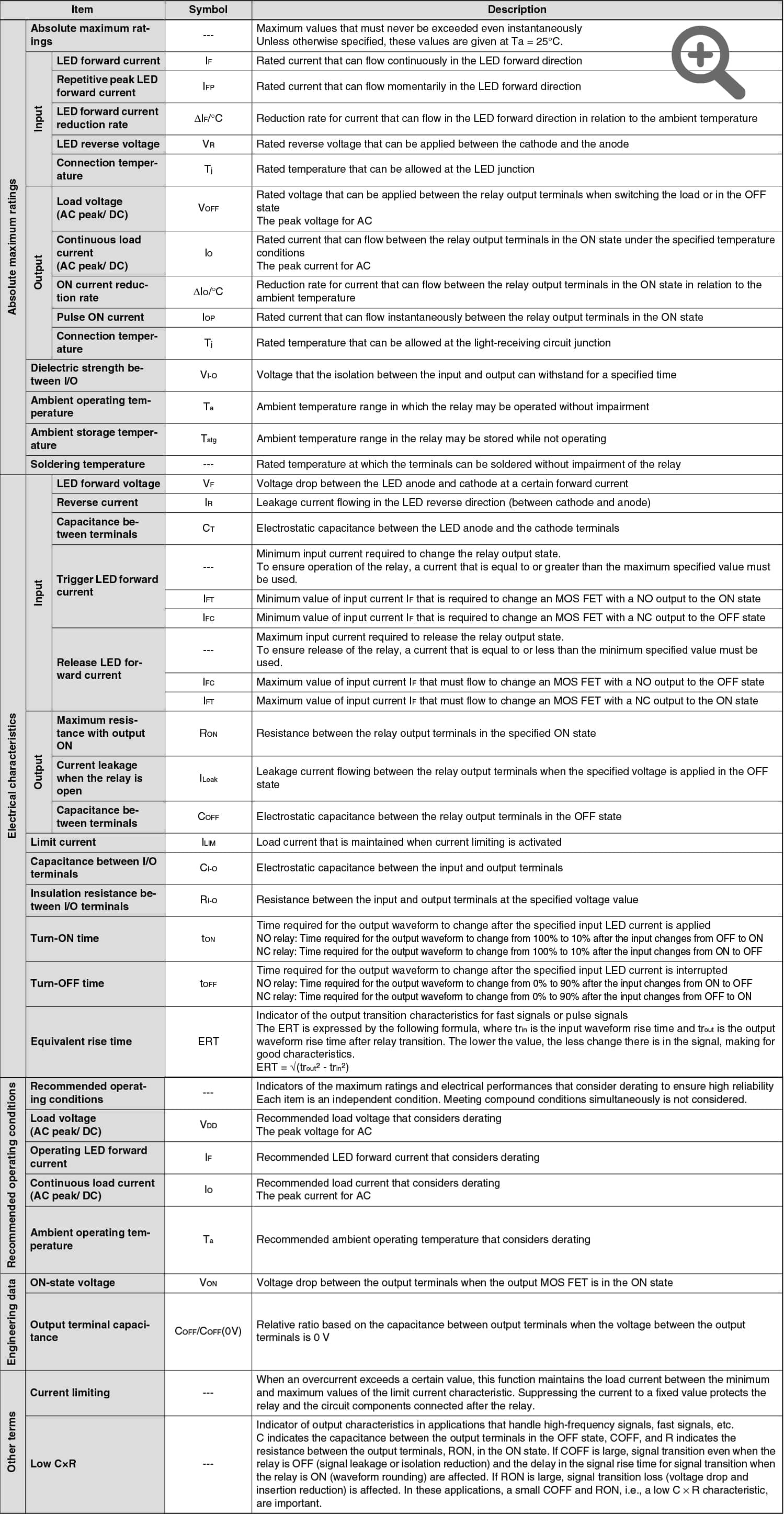
Common Terminology in MOS FET Relay Product Catalog
Explains the terms used in the MOS FET relay datasheet.
- Basics
- Technology
- General Application
- Glossary