Describes the unique characteristics of electronic components, malfunction causes and measures, in an easy-to-understand manner.
It can also be used as a preliminary prevention measure and a primary consultation tool when trouble occurs at any time.
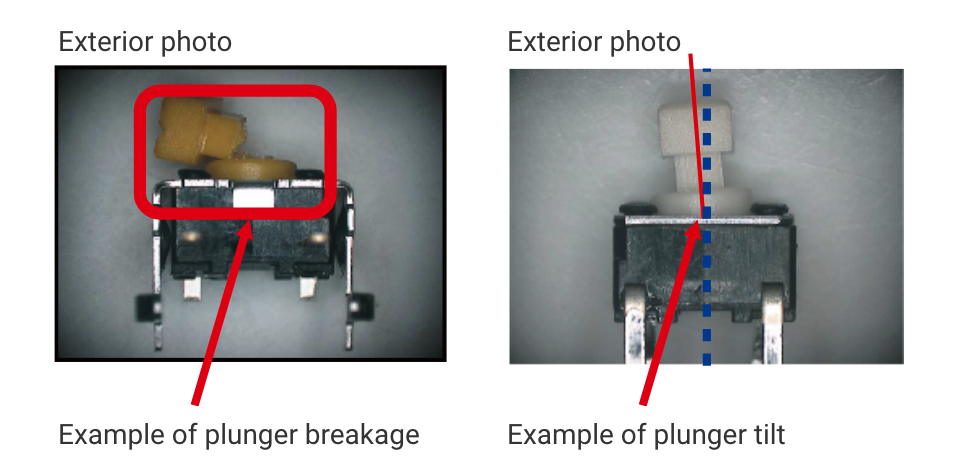
Defect case studies
You can understand specific examples of defects that can be assumed from a particular phenomenon with photos.
Checkpoints for Prevention
Easy-to-understand explanations with illustrations are provided to avoid problems when setting up the product.
A must-have guide for your benefit. We have prepared PDFs for each product, so please download and use them.
* In case of a malfunction occurring, please return the part(s) to us as is (do not take it/them apart).
MOS FET Relay

Click to read contents
Contents
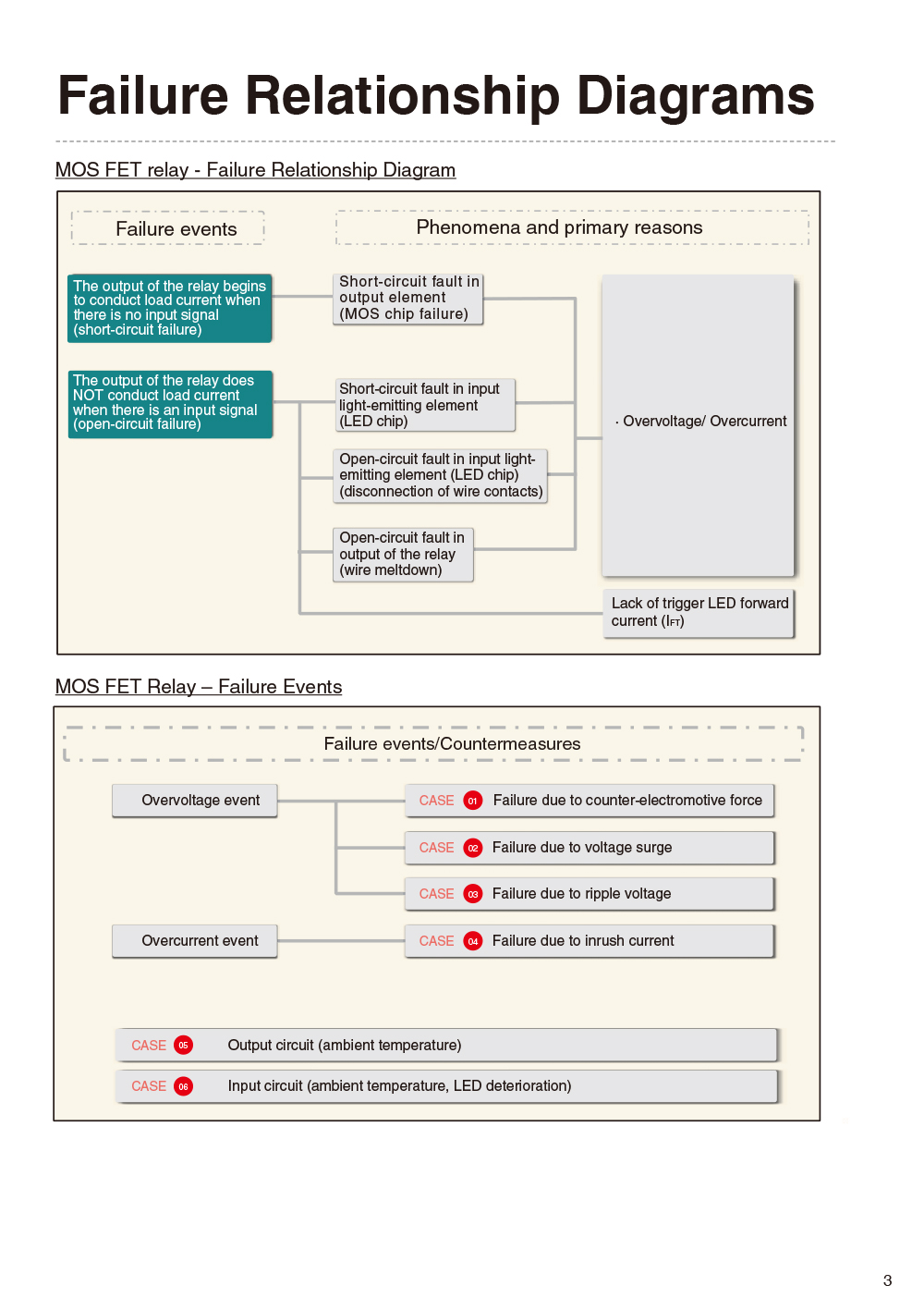
- MOS FET Relay - Failure Relationship Diagrams
- MOS FET Relay - Failure Events
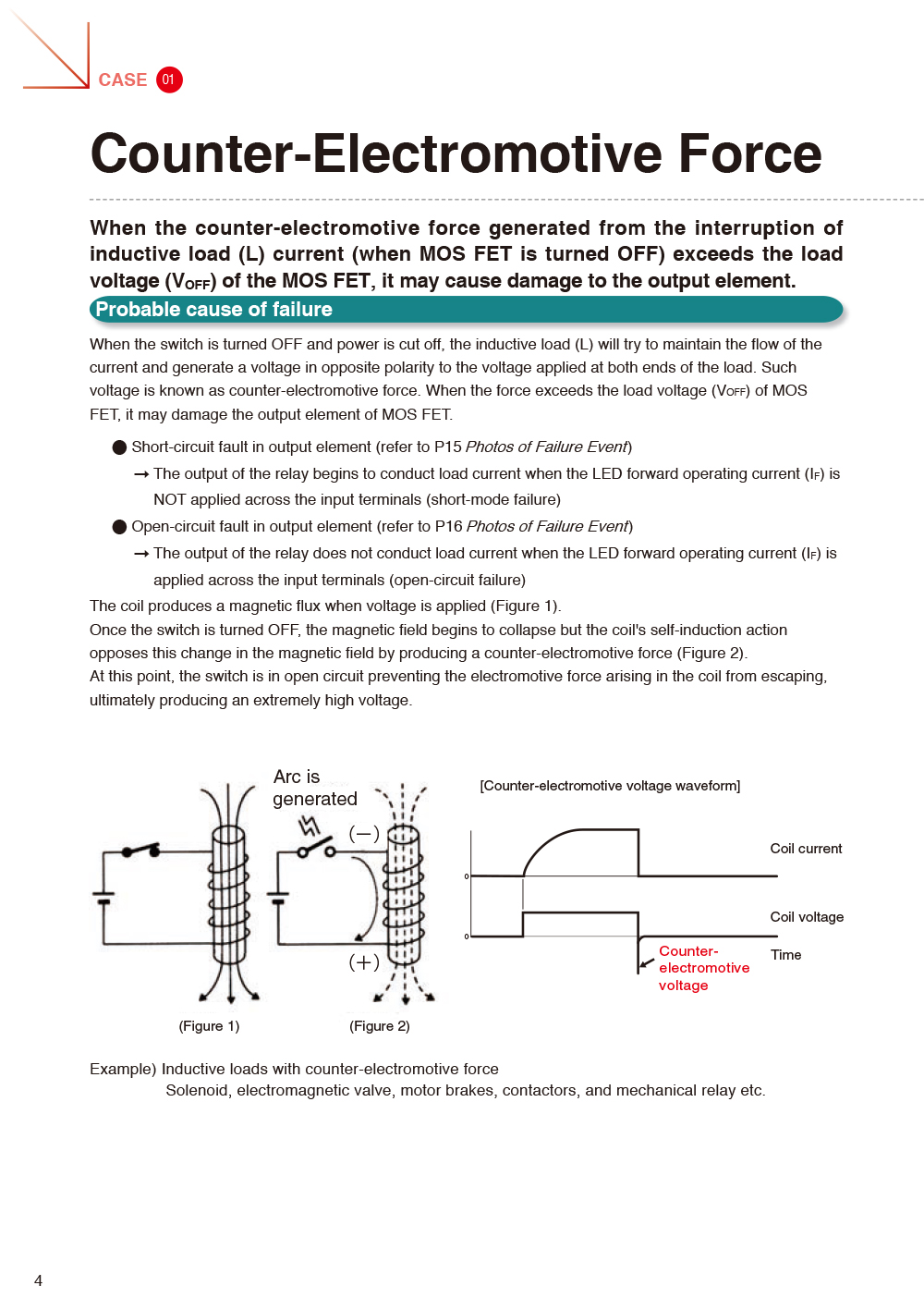
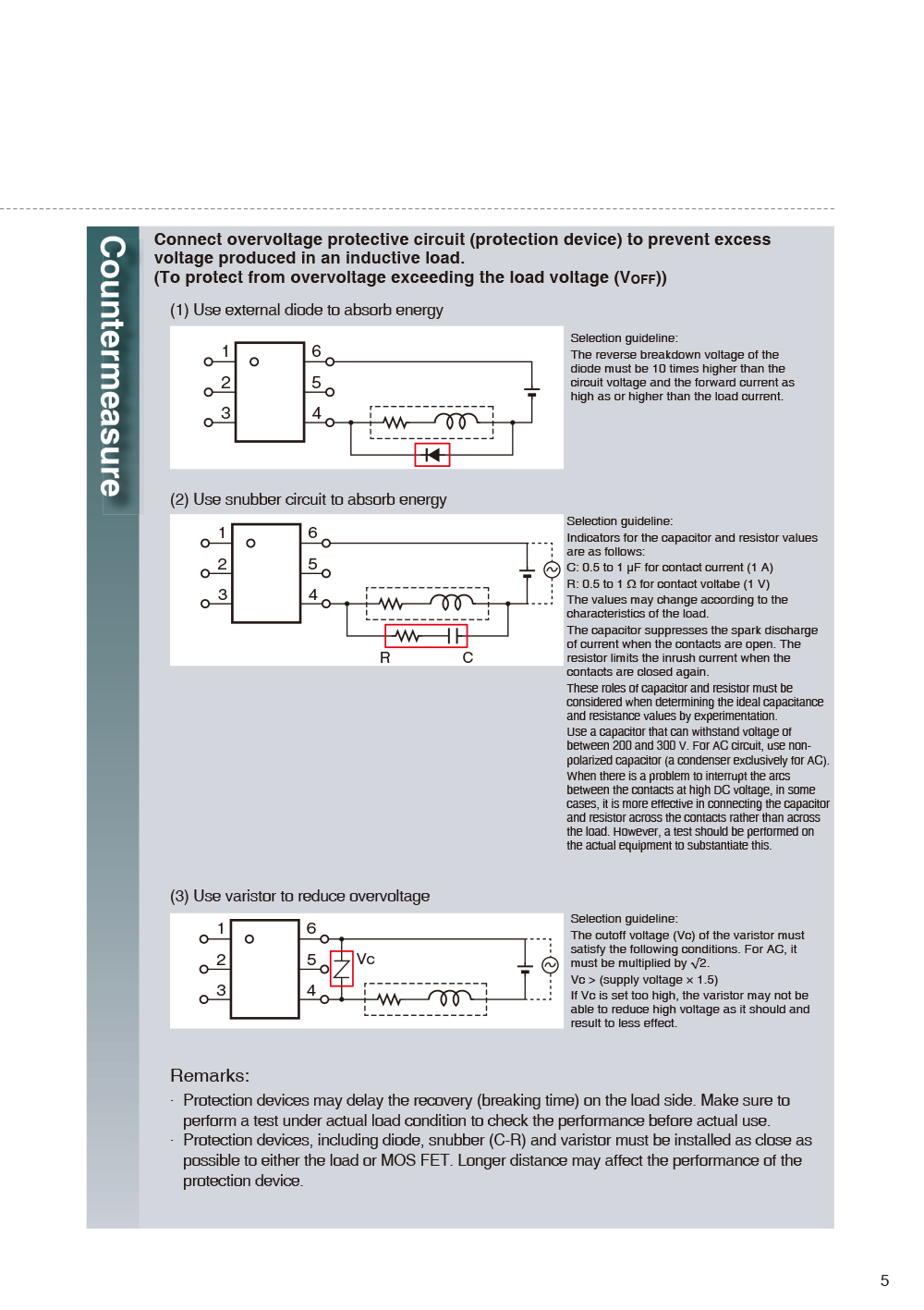
- CASE01 Counter-Electromotive Force
- CASE02 Voltage Surge (Input Side)
- CASE03 Ripple voltage
- CASE04 Inrush Current
- CASE05 Output Circuit Design Guideline
- CASE06 Input Circuit Design Guideline
- Photos of Failure Event
Mechanical PCB Relay Edition

Click to read contents
Contents
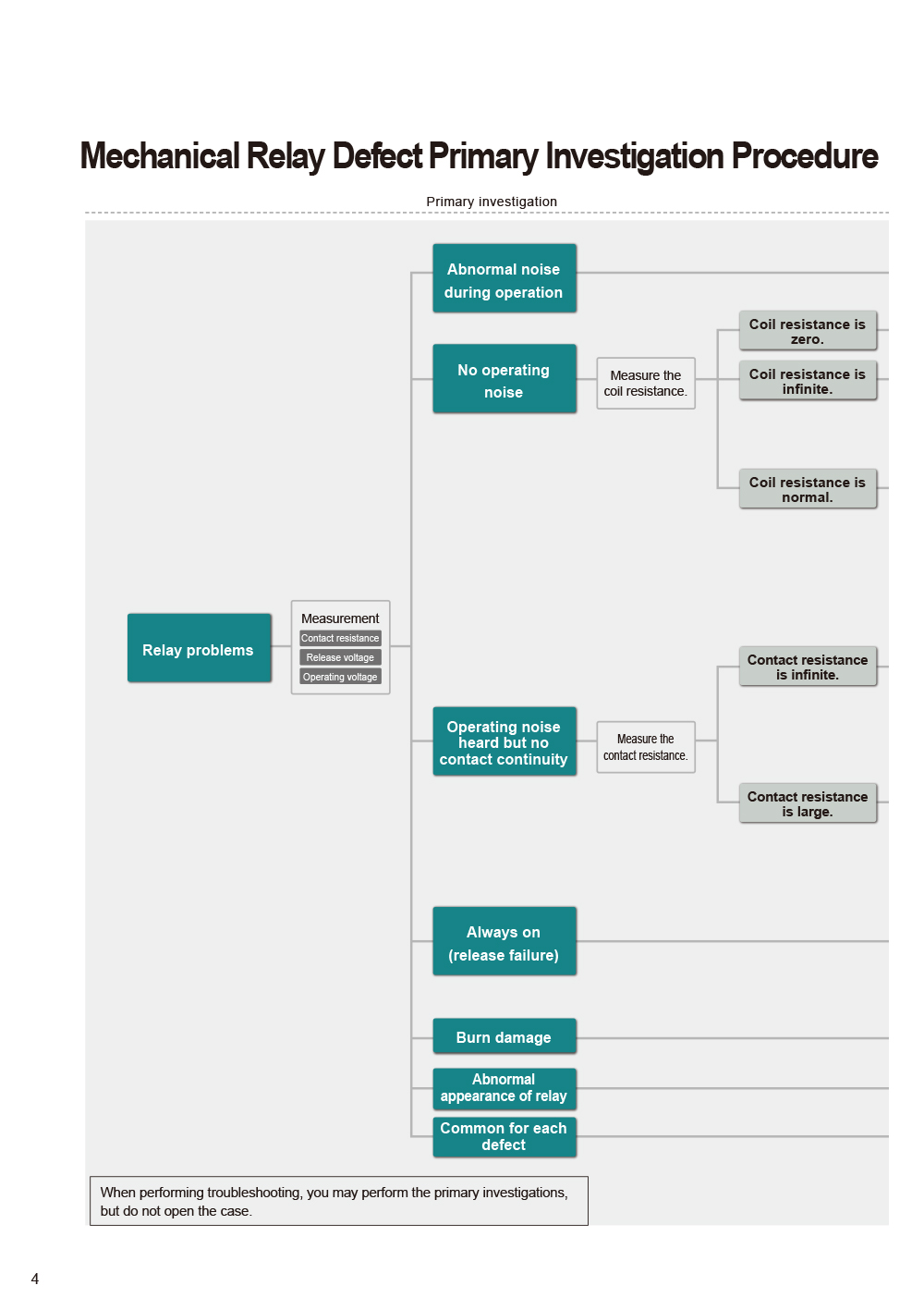
- Mechanical Relay Defect Primary Investigation Procedure
- CASE01 Buzzing and Vibration (AC Only)
- CASE02 Short Circuit Failure of Diode for Relay Coil Surge Absorber
- CASE03 Abnormal Heat Generation
- CASE04 Layer Short Circuit
- CASE05 Contact Welding
- CASE06 Contact Sticking (Contact Gluing)
- CASE07 Operation Failure due to Flux Penetration
- CASE08 Locking due to Contact Transfer
- CASE09 Contact Failure due to Carbonization
- CASE10 Contact Failure due to Silicone
- CASE11 No Contact Follow
- CASE12 Contact Failure due to Sulphurization or Chlorination
- CASE13 Corrosion
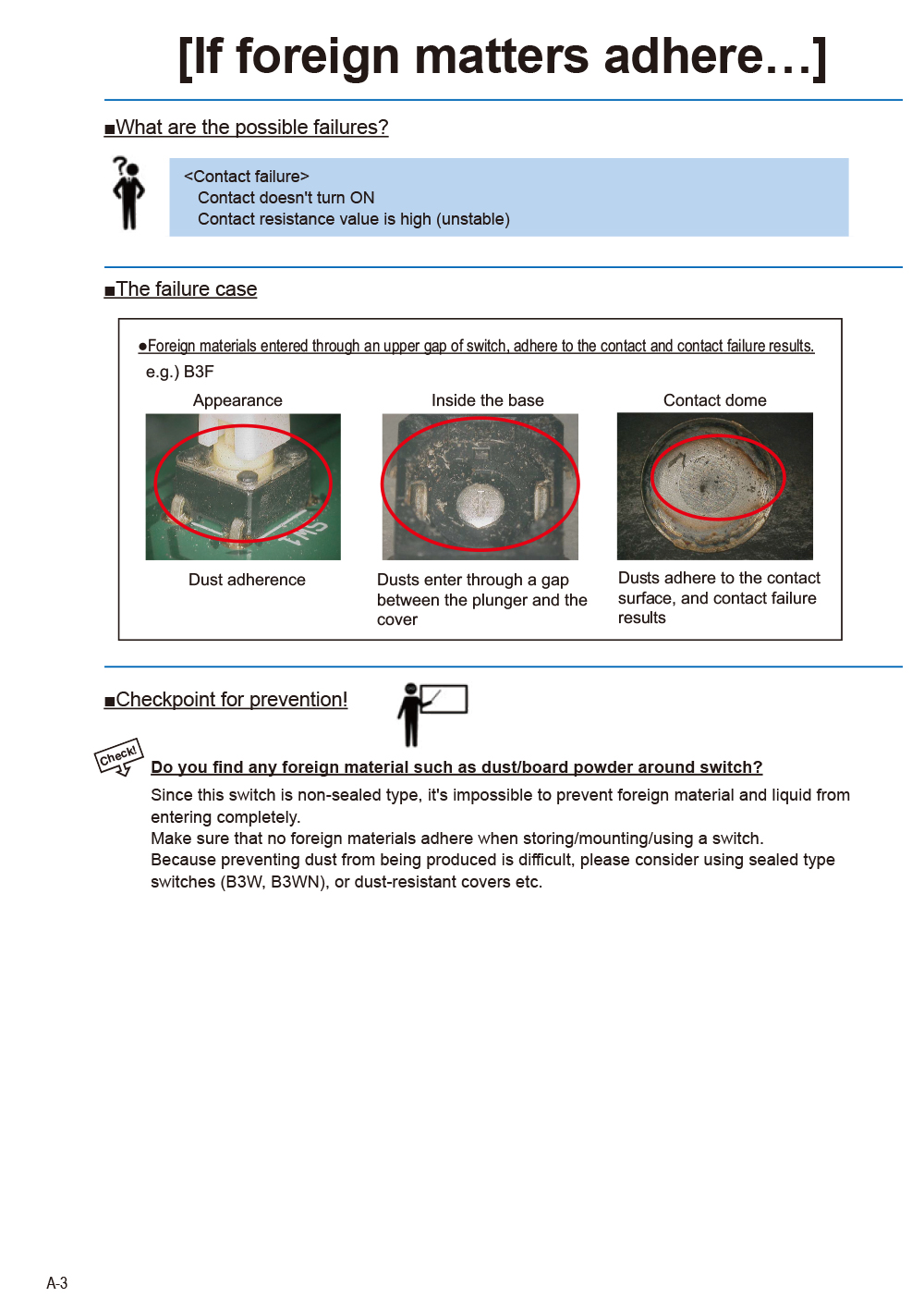
- CASE14 Contact Failure due to the Penetration and Adherence of Foreign Substances (Such as Dust and Insects)
- CASE15 Burn Damage
- CASE16 Wear and Deterioration
- CASE17 Case Holes
- CASE18 Case Swelling
- CASE19 Operation Failure due to Seal Leakage
- Relay Problem Cause Overview
Micro switch

Click to read contents
Contents
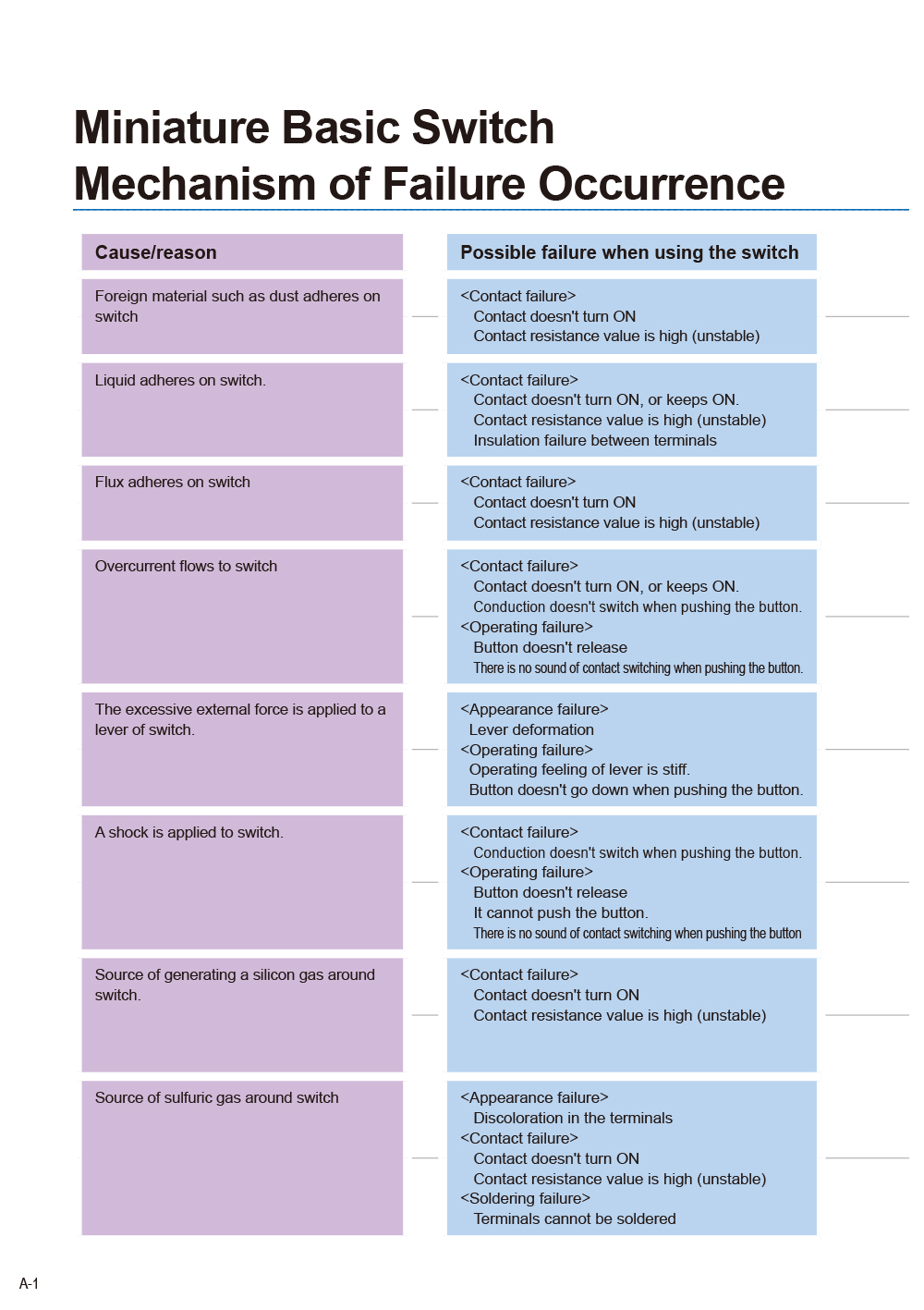
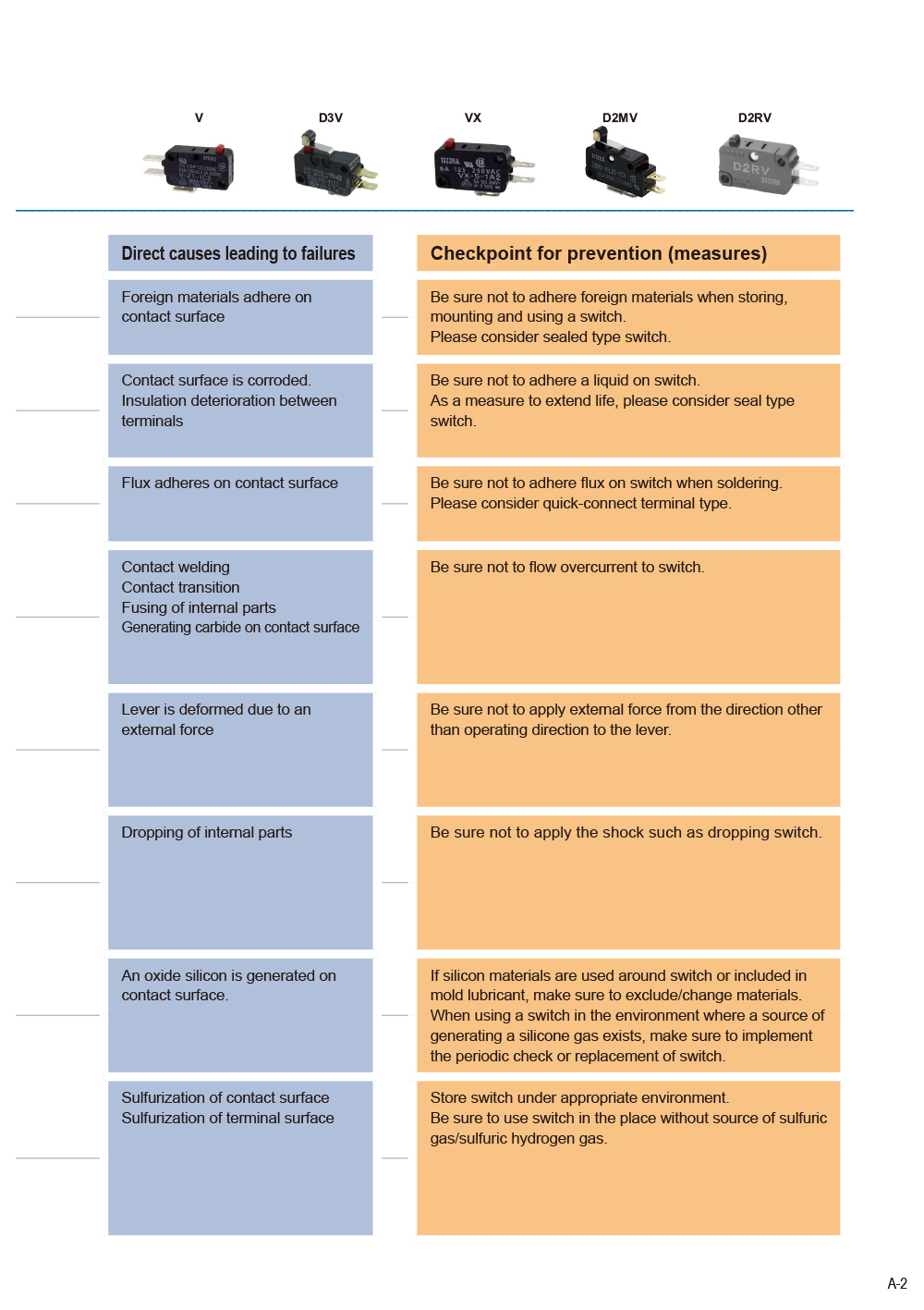
- Miniature Basic Switch
(V, D3V, VX, D2MV, D2RV) - Subminiature Basic Switch
(D3M, SS, SS-P, D2S) - Ultra Subminiature Basic Switch
(D2LS, D2FS, D2FD, D2F, D2MQ) - Sealed Basic Switch
(D2VW, D2SW, D2SW-P, D2HW, D2JW, D2QW) - Detection Switch
(D2A, D3C, D2X) - Reference document
Operation Switch

Click to read contents
Contents
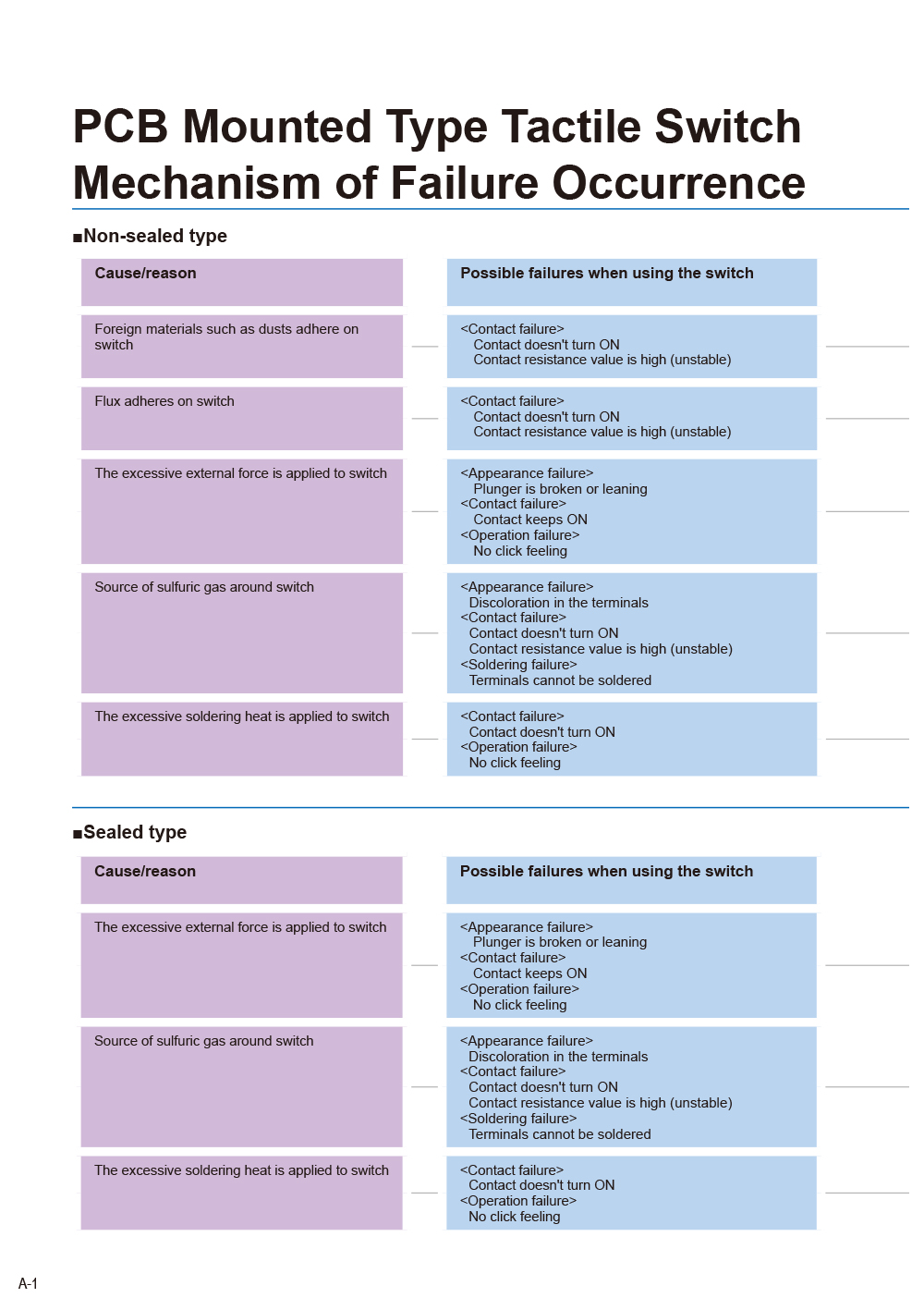
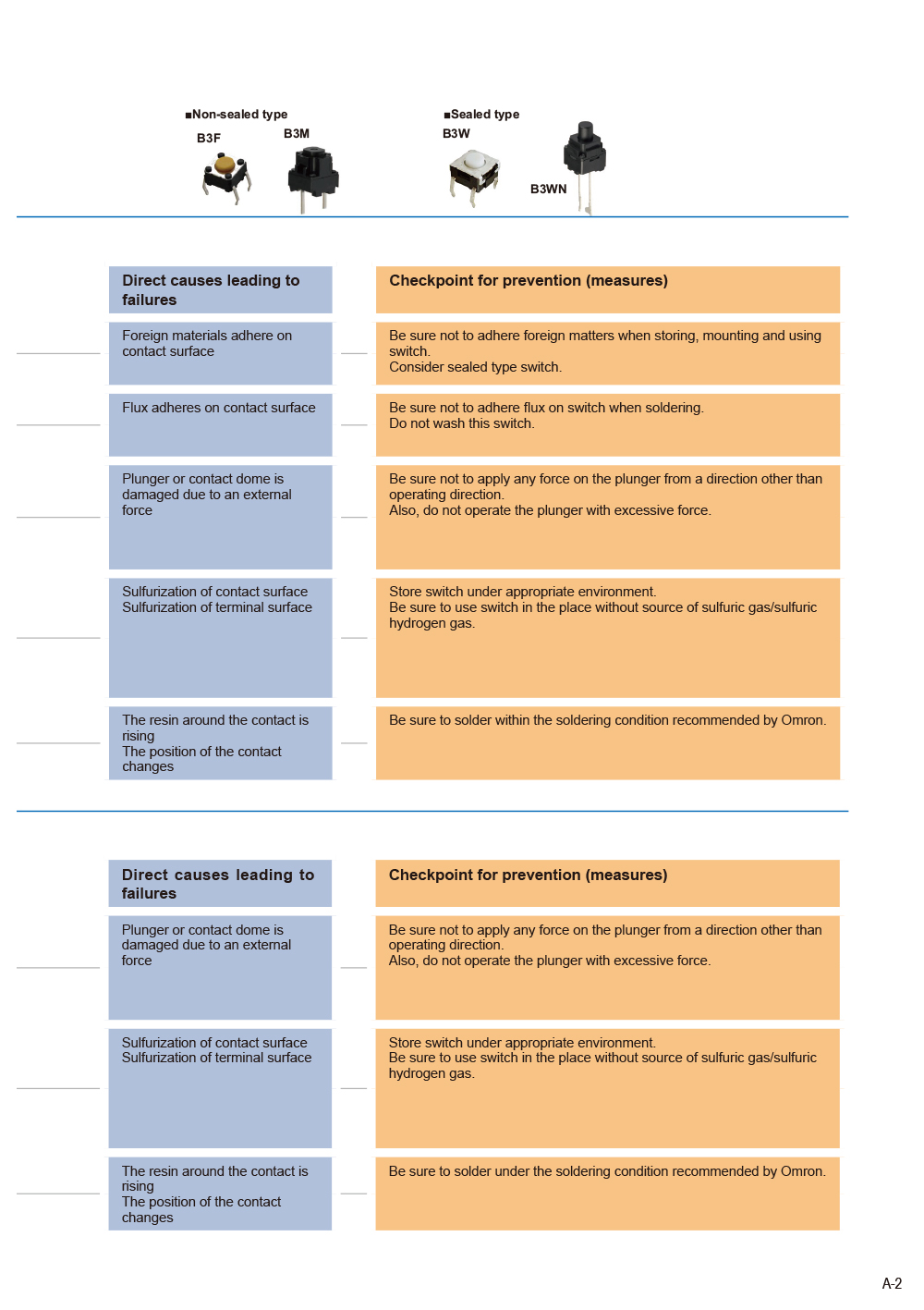
- Tactile Switch [PCB mounted type]
(B3F, B3M, B3W, B3WN) - Tactile Switch [Surface mounted type]
(B3FS, B3U, B3S, B3SN, B3SL) - Rocker Switch
(A8L, A8A, A8G, A8GS) - DIP Switch
- Slide DIP Switch
(A6H, A6HF, A6SH, A6SN, A6T, A6TN, A6D, A6E-N) - Piano DIP Switch
(A6HR, A6SR, A6TR, A6DR, A6FR) - Rotary DIP Switch
(A6K / A6K□, A6R / A6R□, A6A,
A6C / A6CV)
- Slide DIP Switch
- Reference material
Connector

Click to read contents
Contents
- Items Common to All Connectors
- If I Apply a Force to a Terminal...
- If the Electrical Contact Is Deformed...
- If I Apply an External Force After Soldering...
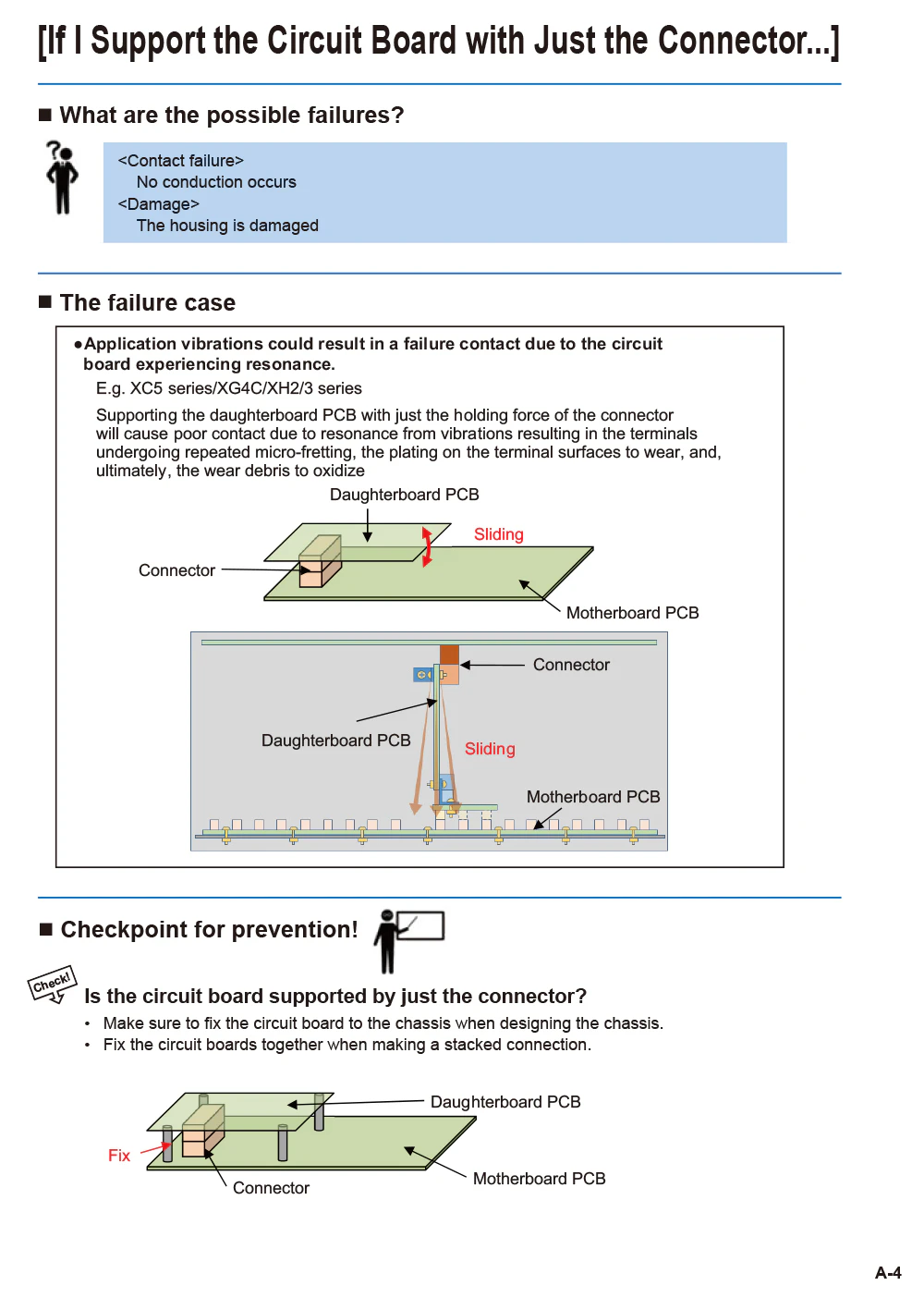
- If I Support the Circuit Board with Just the Connector...
-
FPC/FFC Connectors (XF2, XF3)
- If I Insert the Connector in a Locked State...
- If the Routing of the FPC Is Poor...
- If the Slider Is Held Down Incorrectly...
-
MIL Connectors (XG4, XG5)
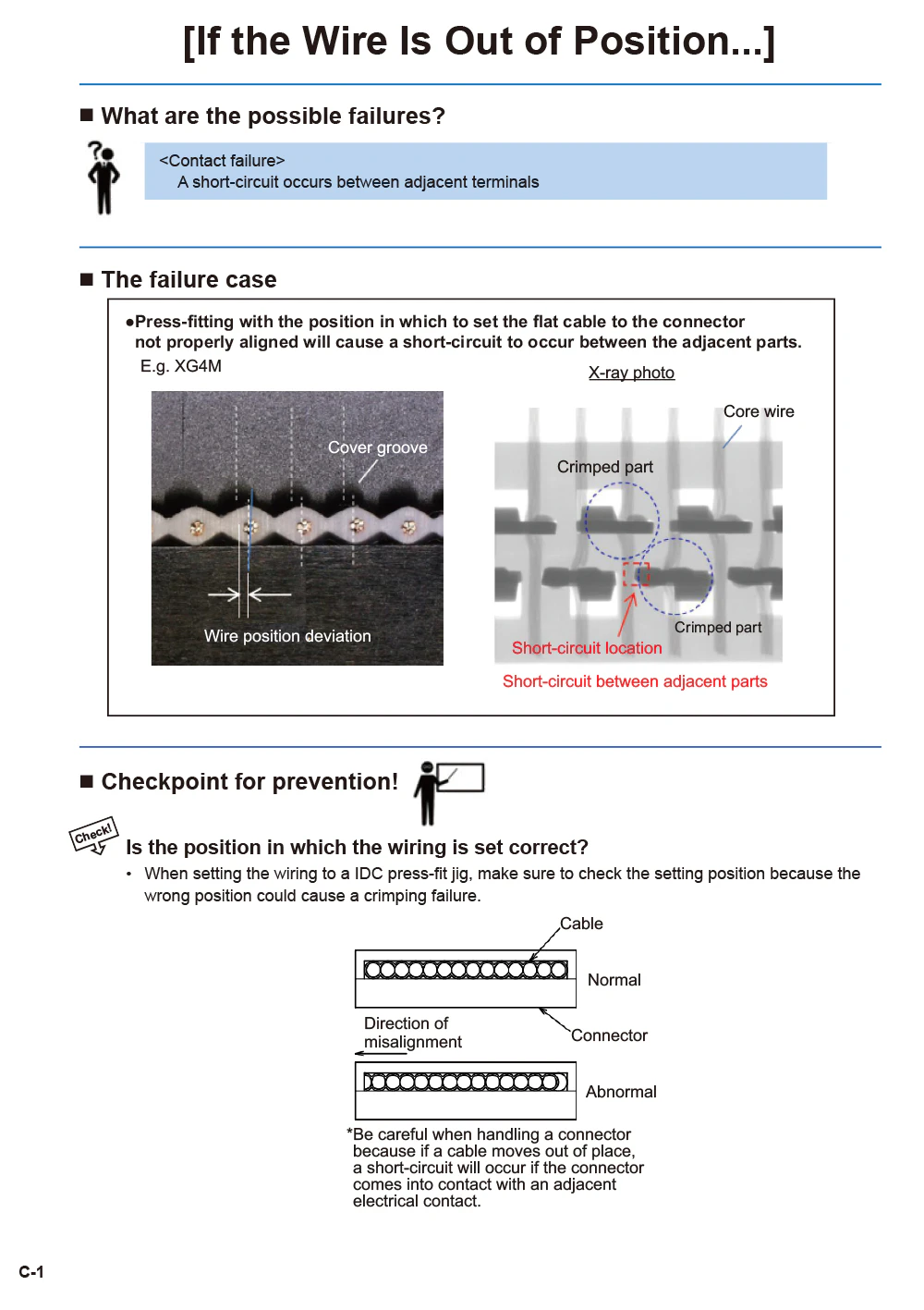
- If the Wire Is Out of Position...
- If I Crimp at an Angle...
- If I Apply an Excessive External Force...
- If I Mistake the Insertion Direction...
- If I Solder in a Half-Locked State...
-
Easy-Wire Connector (e-CON) (XN2)
- If the Wire Twisting Is Insufficient...
- If I Mistake the Wire Specifications...
-
DIN Connectors (XC5, XC8)
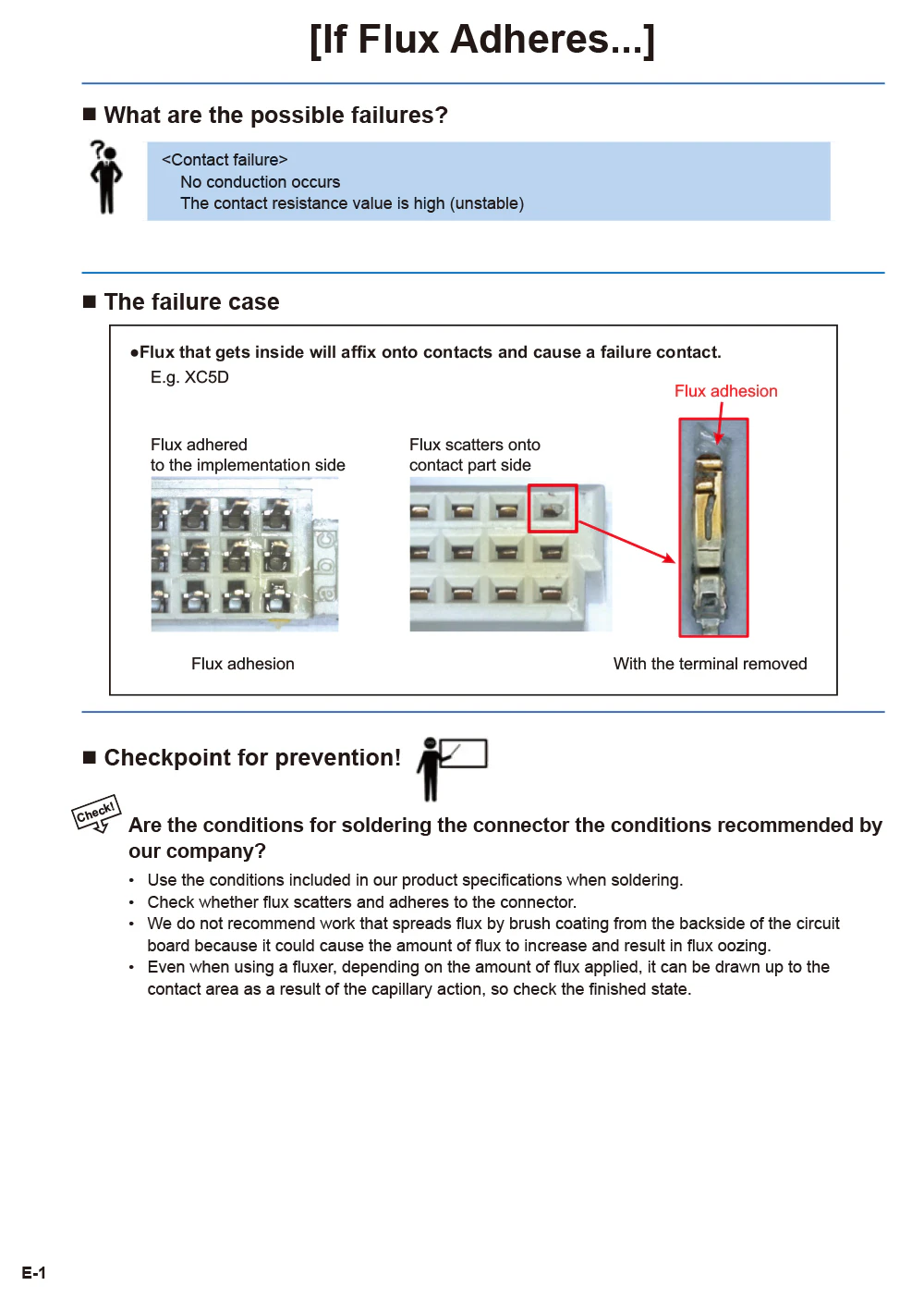
- If Flux Adheres...
- If I Mistake the Tool Settings...
-
Interface Connectors (XM2, XM3)
- If I Process the Shield Braid Incorrectly...
- If the Screw Is Slanted...
-
Reference Materials
- Soldering Procedure
Optical Sensor

Click to read contents
Contents
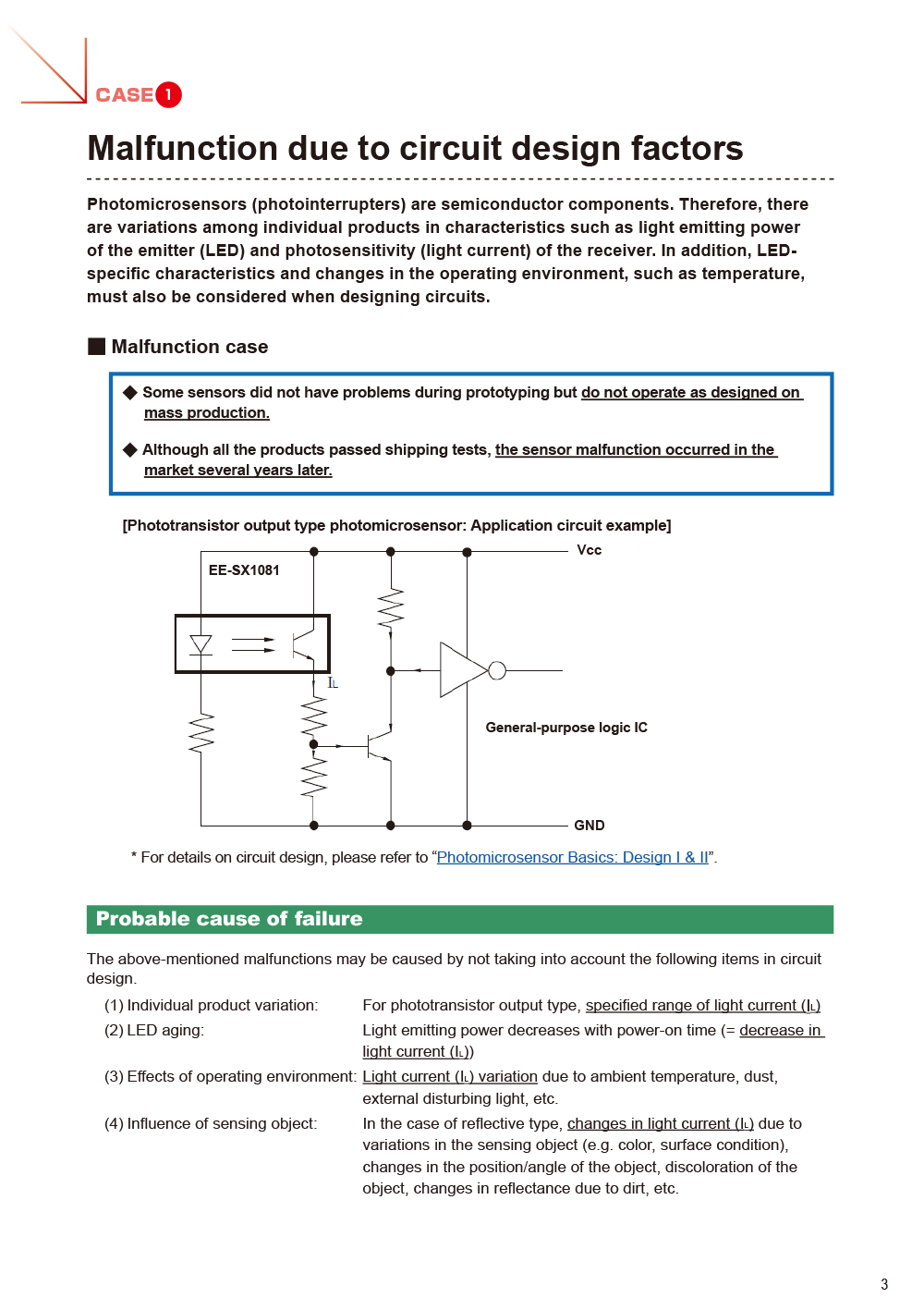
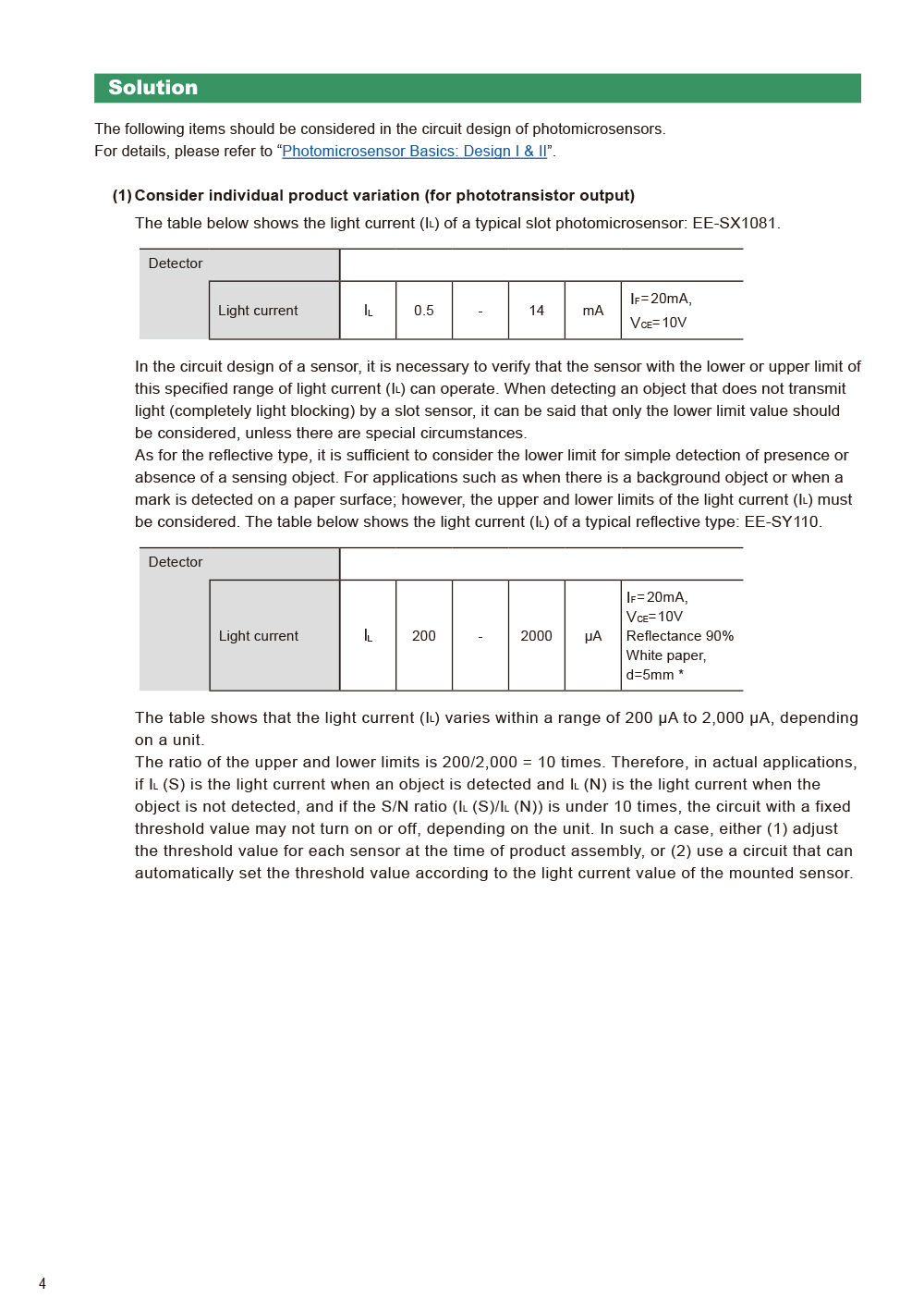
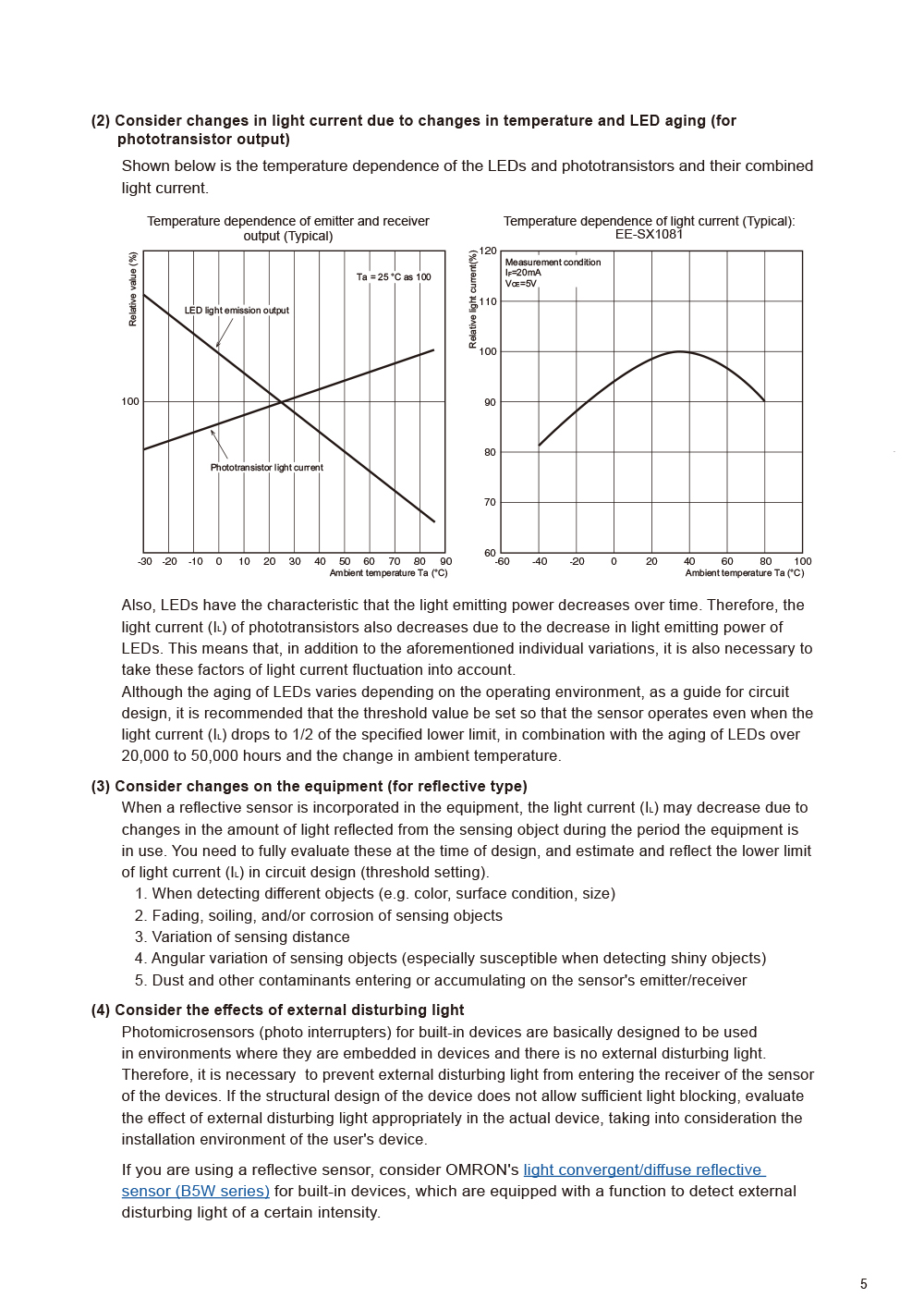
- CASE1 Malfunction due to circuit design factors
(Photomicrosensor) - CASE2 Malfunction due to LED open-circuit failure
(Photomicrosensor) - CASE3 Malfunction due to photo IC chip circuit breakage
(Photomicrosensor) - CASE4 Malfunction due to external disturbing light
(Photomicrosensor) - CASE5 Cracks or fractures in sensor case due to physical deterioration
(Photomicrosensor) - CASE6 Element disconnection due to overheating stress
(Photomicrosensor) - CASE7 Conductive error due to discoloration of lead terminals
(Photomicrosensor) - CASE8 Malfunction due to mutual interference
(Light convergent/diffuse reflective) - CASE9 Malfunction due to transparent cover
(Light convergent/diffuse reflective) - CASE10 Malfunction due to tilted shiny object
(Light convergent reflective)