What is the technical glossary of Photomicrosensors?
ID: FAQE40017E
update:
Answer
There are two kinds of built-in type Photomicrosensors: phototransistor output and photo IC output.
Explanation
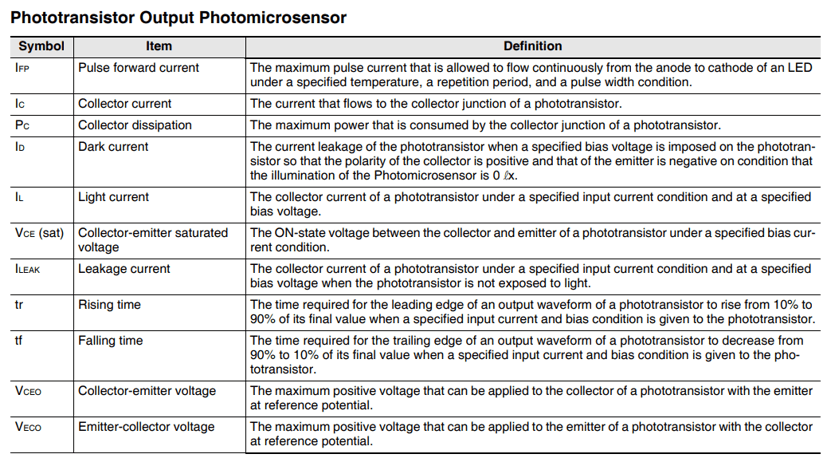
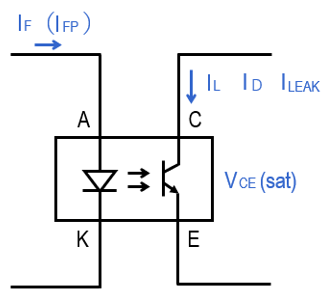
- The table below shows the symbols and terms used in the phototransistor output type Photomicrosensors.
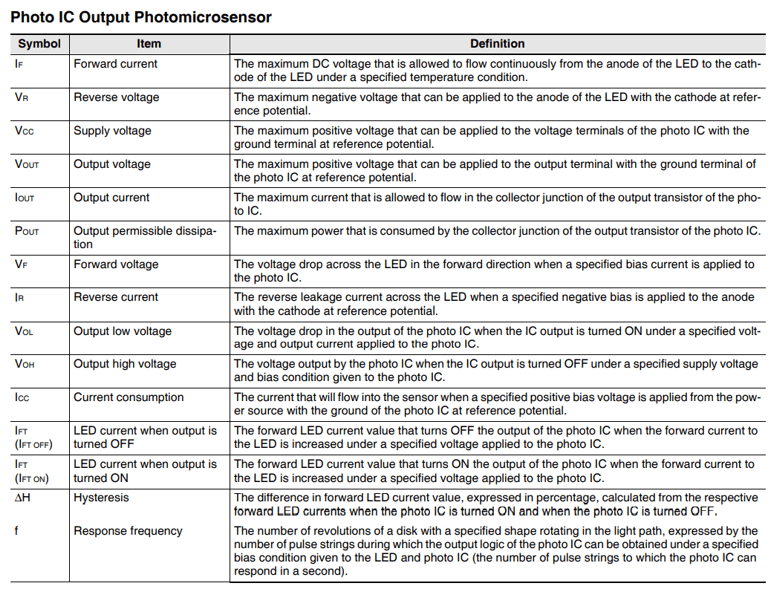
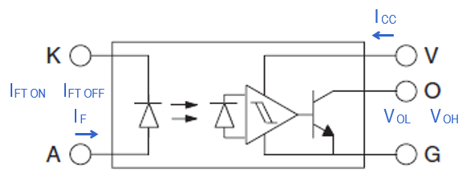
- The table below shows the symbols and terms used in the photo IC output type Photomicrosensors.
For more information, see “Technical Information for Photomicrosensors”
Quick tips
- Phototransistor output type
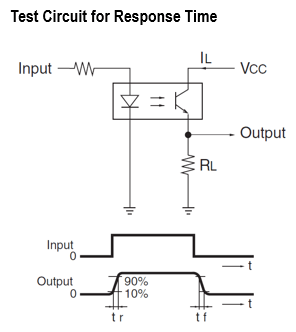
The most important factor in circuit design is the range of light current (IL). The load resistance value (pull-up or pull-down) of the phototransistor side is determined by taking into account the minimum and maximum values and the IL change due to the aging of the LED. In addition, since the response time varies depending on the resistance value, consideration is required for applications such as rotating disk counting. - Photo IC output type
For this output type, the threshold is fixed by the internal circuit. Therefore, the sensitivity of the light receiving element (the receiving light level when the output is turned ON/OFF) is determined by the current (IF) applied to the LED, and is expressed as IFT (ON) or IFT (OFF). This fixed threshold is set as a high sensitivity. It is suitable for applications that do not require fine threshold settings, such as detecting perfectly opaque objects in a transmissive (slot) type, and is effective for applications that require high-speed response.
| Product category | Sensors Photomicro Sensors |
|---|---|
| Classification | Usage, Applications |
| Related keywords |
|